Differential regulation of myc homologs by Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in the early metazoan Hydra
- PMID: 30869835
- PMCID: PMC6618008
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14812
Differential regulation of myc homologs by Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in the early metazoan Hydra
Abstract
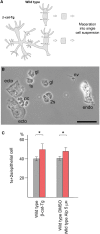
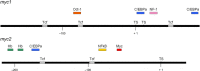
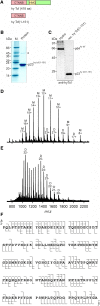
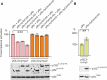
The c-Myc protein is a transcription factor with oncogenic potential controlling fundamental cellular processes. Homologs of the human c-myc protooncogene have been identified in the early diploblastic cnidarian Hydra (myc1, myc2). The ancestral Myc1 and Myc2 proteins display the principal design and biochemical properties of their vertebrate derivatives, suggesting that important Myc functions arose very early in metazoan evolution. c-Myc is part of a transcription factor network regulated by several upstream pathways implicated in oncogenesis and development. One of these signaling cascades is the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway driving cell differentiation and developmental patterning, but also tumorigenic processes including aberrant transcriptional activation of c-myc in several human cancers. Here, we show that genetic or pharmacological stimulation of Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in Hydra is accompanied by specific downregulation of myc1 at mRNA and protein levels. The myc1 and myc2 promoter regions contain consensus binding sites for the transcription factor Tcf, and Hydra Tcf binds to the regulatory regions of both promoters. The myc1 promoter is also specifically repressed in the presence of ectopic Hydra β-Catenin/Tcf in avian cell culture. We propose that Hydra myc1 is a negative Wnt signaling target, in contrast to vertebrate c-myc, which is one of the best studied genes activated by this pathway. On the contrary, myc2 is not suppressed by ectopic β-Catenin in Hydra and presumably represents the structural and functional c-myc ortholog. Our data implicate that the connection between β-Catenin-mediated signaling and myc1 and myc2 gene regulation is an ancestral metazoan feature. Its impact on decision making in Hydra interstitial stem cells is discussed.
Keywords: cnidarian; development; gene regulation; oncogene; signal transduction.
© 2019 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
High Intrinsic Oncogenic Potential in the Myc-Box-Deficient Hydra Myc3 Protein.Cells. 2023 Apr 26;12(9):1265. doi: 10.3390/cells12091265. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174665 Free PMC article.
-
Hydra myc2, a unique pre-bilaterian member of the myc gene family, is activated in cell proliferation and gametogenesis.Biol Open. 2014 Apr 25;3(5):397-407. doi: 10.1242/bio.20147005. Biol Open. 2014. PMID: 24771621 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell-specific activation of an ancestral myc protooncogene with conserved basic functions in the early metazoan Hydra.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 2;107(9):4051-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911060107. Epub 2010 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20142507 Free PMC article.
-
The Yin-Yang of TCF/beta-catenin signaling.Adv Cancer Res. 2000;77:1-24. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60783-6. Adv Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10549354 Review.
-
TCF: Lady Justice casting the final verdict on the outcome of Wnt signalling.Biol Chem. 2002 Feb;383(2):255-61. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.027. Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11934263 Review.
Cited by
-
MYC Analysis in Cancer and Evolution.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2318:87-117. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1476-1_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34019288
-
A pan-metazoan concept for adult stem cells: the wobbling Penrose landscape.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022 Feb;97(1):299-325. doi: 10.1111/brv.12801. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2022. PMID: 34617397 Free PMC article.
-
Articulating the "stem cell niche" paradigm through the lens of non-model aquatic invertebrates.BMC Biol. 2022 Jan 20;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01230-5. BMC Biol. 2022. PMID: 35057814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Intrinsic Oncogenic Potential in the Myc-Box-Deficient Hydra Myc3 Protein.Cells. 2023 Apr 26;12(9):1265. doi: 10.3390/cells12091265. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174665 Free PMC article.
-
Changes of cell-type diversity in the polyp-to-medusa metagenesis of the scyphozoan jellyfish Aurelia coerulea (formerly sp.1).bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 15:2023.08.24.554571. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.554571. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39990407 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Bister K & Jansen HW (1986) Oncogenes in retroviruses and cells: biochemistry and molecular genetics. Adv Cancer Res 47, 99–188. - PubMed
-
- Eisenman RN (2001) Deconstructing myc. Genes Dev 15, 2023–2030. - PubMed
-
- Adhikary S & Eilers M (2005) Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6, 635–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

