Recurrent herpes simplex virus-1 infection induces hallmarks of neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits in mice
- PMID: 30870531
- PMCID: PMC6417650
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007617
Recurrent herpes simplex virus-1 infection induces hallmarks of neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits in mice
Abstract
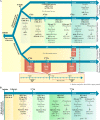
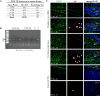
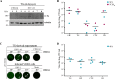
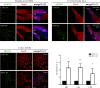
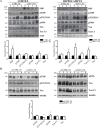
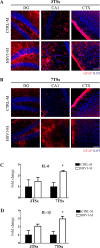
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a DNA neurotropic virus, usually establishing latent infections in the trigeminal ganglia followed by periodic reactivations. Although numerous findings suggested potential links between HSV-1 and Alzheimer's disease (AD), a causal relation has not been demonstrated yet. Hence, we set up a model of recurrent HSV-1 infection in mice undergoing repeated cycles of viral reactivation. By virological and molecular analyses we found: i) HSV-1 spreading and replication in different brain regions after thermal stress-induced virus reactivations; ii) accumulation of AD hallmarks including amyloid-β protein, tau hyperphosphorylation, and neuroinflammation markers (astrogliosis, IL-1β and IL-6). Remarkably, the progressive accumulation of AD molecular biomarkers in neocortex and hippocampus of HSV-1 infected mice, triggered by repeated virus reactivations, correlated with increasing cognitive deficits becoming irreversible after seven cycles of reactivation. Collectively, our findings provide evidence that mild and recurrent HSV-1 infections in the central nervous system produce an AD-like phenotype and suggest that they are a risk factor for AD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Roizman B, Knipe DM. Herpes simplex virus and their replication In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology: Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2001. p. 2432–4.
-
- Kastrukoff L, Hamada T, Schumacher U, Long C, Doherty PC, Koprowski H. Central nervous system infection and immune response in mice inoculated into the lip with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Neuroimmunol. 1982;2(3–4):295–305. - PubMed
-
- Lewandowski G, Zimmerman MN, Denk LL, Porter DD, Prince GA. Herpes simplex type 1 infects and establishes latency in the brain and trigeminal ganglia during primary infection of the lip in cotton rats and mice. Arch Virol. 2002;147(1):167–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

