Association of Protein Intake in Three Meals with Muscle Mass in Healthy Young Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 30871197
- PMCID: PMC6471574
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11030612
Association of Protein Intake in Three Meals with Muscle Mass in Healthy Young Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
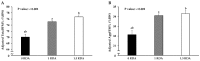
Protein intake of >0.24 g/kg of body weight (BW) at a single meal is necessary to maximize muscle protein synthesis in a young population. However, the association between the protein intake rate for three meals and muscle mass in the young population has not been evaluated. We hypothesized that a protein intake of >0.24 g/kg BW at all three meals is effective for maintaining muscle mass. Therefore, we cross-sectionally examined the association between protein intake at all three meals with muscle mass in 266 healthy young subjects (aged 21.4 ± 2.4 years). Subjects were divided into the AP group, which achieved protein intake >0.24 g/kg BW at all three meals; and the NP group, which did not. We calculated total fat-free mass (FFM) and appendicular fat-free mass (AppFFM) with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and the percentage of total FFM (TotalFFM%) and appendicular FFM (AppFFM%) were calculated as the percentage of BW (%BW). We demonstrated that TotalFFM% (77.0 ± 0.5 vs. 75.2 ± 0.4%, p = 0.008) and AppFFM% (34.7 ± 0.3 vs. 34.1 ± 0.2%, p = 0.058) were higher in the AP than in the NP group. This finding suggests that achieving protein intake of >0.24 g/kg BW at all three meals is important for muscle mass maintenance in young populations.
Keywords: DXA; appendicular fat-free mass; cross-sectional study; dietary records; dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; fat-free mass; muscle mass; protein intake; young subjects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

