Steroidogenic Factor 1 (Nr5a1) is Required for Sertoli Cell Survival Post Sex Determination
- PMID: 30872705
- PMCID: PMC6418149
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-41051-1
Steroidogenic Factor 1 (Nr5a1) is Required for Sertoli Cell Survival Post Sex Determination
Abstract
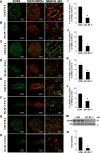
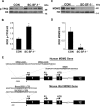
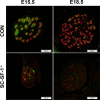
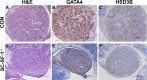
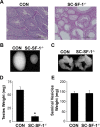
The elevated level of Steroidogenic Factor 1 (Nr5a1, Sf-1) expression in the male gonadal development pathway, post sex determination, implies a vital role in testis gonadal differentiation. In this study we generated Sertoli cell-specific Nr5a1 KO mice (SC-SF-1-/-) at E14.5, which coincides with testis development post sex determination, using the Amh-Cre mouse model. Analysis of SC-SF-1-/- (Sertoli cell specific Nr5a1 knockout) testes demonstrated apoptosis as early as E15. Further analysis revealed that SC-SF-1-/- gonads displayed lower MDM2 levels resulting in elevated TP53 levels, which we believe may lead to apoptosis of the Sertoli cell population, inferring the possibility that NR5A1 directly regulates MDM2 expression. By E15.5, the Sertoli cell and germ cell population declined in SC-SF-1-/- mice resulting in the disruption of seminiferous cords with limited cord structure remaining at E18.5. Due to the loss of Sertoli and germ cells, the testis weights of SC-SF-1-/- mice at 6-weeks were much reduced; however, SC-SF-1-/- seminal vesicles weights were comparable suggesting intact Leydig cell androgen production. We conclude that NR5A1 regulates the TP53 pathway during development, is essential for fetal Sertoli cell survival and controls the cell cycle of Sertoli cells during differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Morohashi K, Honda S, Inomata Y, Handa H, Omura T. A common trans-acting factor, Ad4-binding protein, to the promoters of steroidogenic P-450s. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:17913–17919. - PubMed
-
- Sadovsky Y, et al. Mice deficient in the orphan receptor steroidogenic factor 1 lack adrenal glands and gonads but express P450 side-chain-cleavage enzyme in the placenta and have normal embryonic serum levels of corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:10939–10943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.24.10939. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

