Silencing of lncRNA PKIA-AS1 Attenuates Spinal Nerve Ligation-Induced Neuropathic Pain Through Epigenetic Downregulation of CDK6 Expression
- PMID: 30873006
- PMCID: PMC6401634
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00050
Silencing of lncRNA PKIA-AS1 Attenuates Spinal Nerve Ligation-Induced Neuropathic Pain Through Epigenetic Downregulation of CDK6 Expression
Abstract
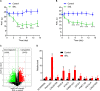
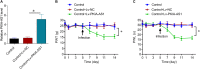
Neuropathic pain (NP) is among the most intractable comorbidities of spinal cord injury. Dysregulation of non-coding RNAs has also been implicated in the development of neuropathic pain. Here, we identified a novel lncRNA, PKIA-AS1, by using lncRNA array analysis in spinal cord tissue of spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model rats, and investigated the role of PKIA-AS1 in SNL-mediated neuropathic pain. We observed that PKIA-AS1 was significantly upregulated in SNL model rats and that PKIA-AS1 knockdown attenuated neuropathic pain progression. Alternatively, overexpression of PKIA-AS1 was sufficient to induce neuropathic pain-like symptoms in uninjured rats. We also found that PKIA-AS1 mediated SNL-induced neuropathic pain by directly regulating the expression and function of CDK6, which is essential for the initiation and maintenance of neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain. Therefore, our study identifies PKIA-AS1 as a novel therapeutic target for neuroinflammation related neuropathic pain.
Keywords: CDK6; long non-coding RNA; neuroinflammation; neuropathic pain; spinal cord injury.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

