The Role of Connexin and Pannexin Channels in Perinatal Brain Injury and Inflammation
- PMID: 30873043
- PMCID: PMC6400979
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00141
The Role of Connexin and Pannexin Channels in Perinatal Brain Injury and Inflammation
Abstract
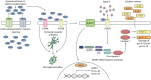
Perinatal brain injury remains a major cause of death and life-long disability. Perinatal brain injury is typically associated with hypoxia-ischemia and/or infection/inflammation. Both hypoxia-ischemia and infection trigger an inflammatory response in the brain. The inflammatory response can contribute to brain cell loss and chronic neuroinflammation leading to neurological impairments. It is now well-established that brain injury evolves over time, and shows a striking spread from injured to previously uninjured regions of the brain. There is increasing evidence that this spread is related to opening of connexin hemichannels and pannexin channels, both of which are large conductance membrane channels found in almost all cell types in the brain. Blocking connexin hemichannels within the first 3 h after hypoxia-ischemia has been shown to improve outcomes in term equivalent fetal sheep but it is important to also understand the downstream pathways linking membrane channel opening with the development of injury in order to identify new therapeutic targets. Open membrane channels release adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and other neuroactive molecules, into the extracellular space. ATP has an important physiological role, but has also been reported to act as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) signal mediated through specific purinergic receptors and so act as a primary signal 1 in the innate immune system inflammasome pathway. More crucially, extracellular ATP is a key inflammasome signal 2 activator, with purinergic receptor binding triggering the assembly of the multi-protein inflammasome complex. The inflammasome pathway and complex formation contribute to activation of inflammatory caspases, and the release of inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-18, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). We propose that the NOD-like receptor protein-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, which has been linked to inflammatory responses in models of ischemic stroke and various inflammatory diseases, may be one mechanism by which connexin hemichannel opening especially mediates perinatal brain injury.
Keywords: ATP; connexin; hemichannel; inflammasome; inflammation; ischemia; pannexin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Connexins, Pannexins and Gap Junctions in Perinatal Brain Injury.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 18;10(6):1445. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061445. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glia and hemichannels: key mediators of perinatal encephalopathy.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Feb;13(2):181-189. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.226378. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 29557357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inflammasome pathway is amplified and perpetuated in an autocrine manner through connexin43 hemichannel mediated ATP release.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Mar;1862(3):385-393. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.11.015. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 29158134
-
Role of Hemichannels in CNS Inflammation and the Inflammasome Pathway.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2016;104:1-37. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 31. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27038371 Review.
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
Cited by
-
Prickly Ash Seeds improve immunity of Hu sheep by changing the diversity and structure of gut microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1273714. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1273714. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029081 Free PMC article.
-
Periventricular Microglia Polarization and Morphological Changes Accompany NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neuroinflammation after Hypoxic-Ischemic White Matter Damage in Premature Rats.J Immunol Res. 2023 Aug 19;2023:5149306. doi: 10.1155/2023/5149306. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 37636861 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Connexin-43 Hemichannels and Pannexin1 Channels: Provocative Antiarrhythmic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 29;22(1):260. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010260. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33383853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on acupuncture treatment in central nervous system diseases based on NLRP3 inflammasome in animal models.Front Neurosci. 2023 Feb 28;17:1118508. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1118508. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36925735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation-Based Quantitative Serum Proteomics Analysis in Ischemic Stroke Patients With Hemorrhagic Transformation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Aug 25;15:710129. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.710129. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34512266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aróstegui J. I., Lopez Saldana M. D., Pascal M., Clemente D., Aymerich M., Balaguer F., et al. . (2010). A somatic NLRP3 mutation as a cause of a sporadic case of chronic infantile neurologic, cutaneous, articular syndrome/neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease: novel evidence of the role of low-level mosaicism as the pathophysiologic mechanism underlying mendelian inherited diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 1158–1166. 10.1002/art.27342 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

