Sudden Cardiac Death in Dialysis: Arrhythmic Mechanisms and the Value of Non-invasive Electrophysiology
- PMID: 30873044
- PMCID: PMC6401645
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00144
Sudden Cardiac Death in Dialysis: Arrhythmic Mechanisms and the Value of Non-invasive Electrophysiology
Abstract
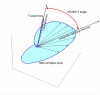
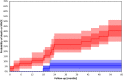
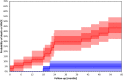
Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) is the leading cause of cardiovascular death in dialysis patients. This review discusses potential underlying arrhythmic mechanisms of SCD in the dialysis population. It examines recent evidence from studies using implantable loop recorders and from electrophysiological studies in experimental animal models of chronic kidney disease. The review summarizes advances in the field of non-invasive electrophysiology for risk prediction in dialysis patients focusing on the predictive value of the QRS-T angle and of the assessments of autonomic imbalance by means of heart rate variability analysis. Future research directions in non-invasive electrophysiology are identified to advance the understanding of the arrhythmic mechanisms. A suggestion is made of incorporation of non-invasive electrophysiology procedures into clinical practice. Key Concepts: - Large prospective studies in dialysis patients with continuous ECG monitoring are required to clarify the underlying arrhythmic mechanisms of SCD in dialysis patients. - Obstructive sleep apnoea may be associated with brady-arrhythmias in dialysis patients. Studies are needed to elucidate the burden and impact of sleeping disorders on arrhythmic complications in dialysis patients. - The QRS-T angle has the potential to be used as a descriptor of uremic cardiomyopathy. - The QRS-T angle can be calculated from routine collected surface ECGs. Multicenter collaboration is required to establish best methodological approach and normal values. - Heart Rate Variability provides indirect assessment of cardiac modulation that may be relevant for cardiac risk prediction in dialysis patients. Short-term recordings with autonomic provocations are likely to overcome the limitations of out of hospital 24-h recordings and should be prospectively assessed.
Keywords: QRS-T angle; TCRT; arrhythmias; dialysis; heart rate variability; implantable loop recorders; sudden cardiac death.
Figures
References
-
- Baigent C., Landray M. J., Reith C., Emberson J., Wheeler D. C., Tomson C., et al. (2011). The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with simvastatin plus ezetimibe in patients with chronic kidney disease (Study of Heart and Renal Protection): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 377 2181–2192. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60739-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnas M. G., Boer W. H., Koomans H. A. (1999). Hemodynamic patterns and spectral analysis of heart rate variability during dialysis hypotension. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10 2577–2584. - PubMed
-
- Berton G., Cordiano R., Cucchini F., Cavuto F., Pellegrinet M., Palatini P. (2009). Atrial fibrillation during acute myocardial infarction: association with all-cause mortality and sudden death after 7-year of follow-up. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 63 712–721. 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02023.x - DOI - PubMed

