Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of T-Cell Epitopes Derived From Potential Th1 Stimulatory Proteins of Leishmania (Leishmania) donovani
- PMID: 30873164
- PMCID: PMC6403406
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00288
Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of T-Cell Epitopes Derived From Potential Th1 Stimulatory Proteins of Leishmania (Leishmania) donovani
Abstract
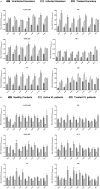
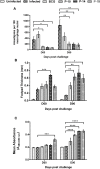
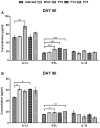
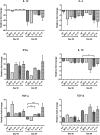
Development of a suitable vaccine against visceral leishmaniasis (VL), a fatal parasitic disease, is considered to be vital for maintaining the success of kala-azar control programs. The fact that Leishmania-infected individuals generate life-long immunity offers a viable proposition in this direction. Our prior studies demonstrated that T-helper1 (Th1) type of cellular response was generated by six potential recombinant proteins viz. elongation factor-2 (elF-2), enolase, aldolase, triose phosphate isomerase (TPI), protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and p45, derived from a soluble antigenic fraction (89.9-97.1 kDa) of Leishmania (Leishmania) donovani promastigote, in treated Leishmania patients and golden hamsters and showed significant prophylactic potential against experimental VL. Moreover, since, it is well-known that our immune system, in general, triggers production of specific protective immunity in response to a small number of amino acids (peptide), this led to the identification of antigenic epitopes of the above-stated proteins utilizing immunoinformatics. Out of thirty-six, three peptides-P-10 (enolase), P-14, and P-15 (TPI) elicited common significant lymphoproliferative as well as Th1-biased cytokine responses both in golden hamsters and human subjects. Further, immunization with these peptides plus BCG offered 75% prophylactic efficacy with boosted cellular immune response in golden hamsters against Leishmania challenge which is indicative of their candidature as potential vaccine candidates.
Keywords: T-cell epitopes; Th1 stimulatory proteins; hamsters; human PBMCs; immunoinformatics; peptides; protective response; visceral leishmaniasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Th1 stimulatory proteins of Leishmania donovani: comparative cellular and protective responses of rTriose phosphate isomerase, rProtein disulfide isomerase and rElongation factor-2 in combination with rHSP70 against visceral leishmaniasis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 30;9(9):e108556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108556. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25268700 Free PMC article.
-
Th1-stimulatory polyproteins of soluble Leishmania donovani promastigotes ranging from 89.9 to 97.1 kDa offers long-lasting protection against experimental visceral leishmaniasis.Vaccine. 2008 Oct 23;26(45):5700-11. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.08.021. Epub 2008 Aug 30. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18762224
-
Characterization of glycolytic enzymes--rAldolase and rEnolase of Leishmania donovani, identified as Th1 stimulatory proteins, for their immunogenicity and immunoprophylactic efficacies against experimental visceral leishmaniasis.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 24;9(1):e86073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086073. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475071 Free PMC article.
-
Leishmaniasis: current status of vaccine development.Curr Mol Med. 2004 Sep;4(6):667-79. doi: 10.2174/1566524043360203. Curr Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15357215 Review.
-
Biomarkers of safety and immune protection for genetically modified live attenuated leishmania vaccines against visceral leishmaniasis - discovery and implications.Front Immunol. 2014 May 23;5:241. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00241. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24904589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design of multi-epitope peptides containing HLA class-I and class-II-restricted epitopes derived from immunogenic Leishmania proteins, and evaluation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses induced in cured cutaneous leishmaniasis subjects.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Mar 16;14(3):e0008093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008093. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32176691 Free PMC article.
-
A Chimera of Th1 Stimulatory Proteins of Leishmania donovani Offers Moderate Immunotherapeutic Efficacy with a Th1-Inclined Immune Response against Visceral Leishmaniasis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 27;2021:8845826. doi: 10.1155/2021/8845826. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34095312 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Polarization Potential of the S. aureus Virulence Factors SplB and GlpQ and Modulation by Adjuvants.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 15;12:642802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.642802. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33936060 Free PMC article.
-
A computer-aided approach to identify novel Leishmania major protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors for treatment of leishmaniasis.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Mar;35(3):297-314. doi: 10.1007/s10822-021-00374-w. Epub 2021 Feb 22. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 33615401
-
Mining the Proteome of Toxoplasma Parasites Seeking Vaccine and Diagnostic Candidates.Animals (Basel). 2022 Apr 23;12(9):1098. doi: 10.3390/ani12091098. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hailu A, Menon JN, Berhe N, Gedamu L, Hassard TH, Kager PA, et al. . Distinct immunity in patients with visceral leishmaniasis from that in subclinically infected and drug-cured people: implications for the mechanism underlying drug cure. J Infect Dis. (2001) 184:112–5. 10.1086/320994 - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO Leishmaniasis. Available online at: http://wwwwhoint/mediacentre/factsheets/fs375/en/ (2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

