Low-Dose Total Body Irradiation Can Enhance Systemic Immune Related Response Induced by Hypo-Fractionated Radiation
- PMID: 30873170
- PMCID: PMC6401363
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00317
Low-Dose Total Body Irradiation Can Enhance Systemic Immune Related Response Induced by Hypo-Fractionated Radiation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Low-Dose Total Body Irradiation Can Enhance Systemic Immune Related Response Induced by Hypo-Fractionated Radiation.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 3;12:745787. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.745787. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34539676 Free PMC article.
Abstract
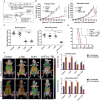
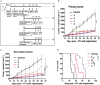
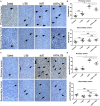
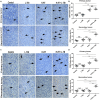
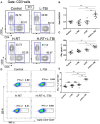
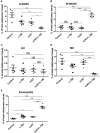
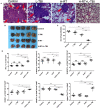
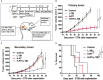
A systemic immune related response (SIME) of radiotherapy has been occasionally observed on metastatic tumors, but the clinical outcomes remain poor. Novel treatment approaches are therefore needed to improve SIME ratio. We used a combination of hypo-fractionated radiation therapy (H-RT) with low-dose total body irradiation (L-TBI) in a syngeneic mouse model of breast and colon carcinoma. The combination therapy of H-RT and L-TBI potentially enhanced SIME by infiltration of CD8+ T cell and altering the immunosuppressive microenvironment in non-irradiated subcutaneous tumor lesions. The frequency of IFN-γ, as a tumor-specific CD8+ T cells producing, significantly inhibited the secondary tumor growth of breast and colon. Our findings suggest that L-TBI could serve as a potential therapeutic agent for metastatic breast and colon cancer and, together with H-RT, their therapeutic potential is enhanced significantly.
Keywords: hypo-fractionated radiation therapy; immune enhancement; immunosuppressive microenvironment; low-dose total body irradiation; systemic immune related response.
Figures
References
-
- Demaria S, Kawashima N, Yang AM, Devitt ML, Babb JS, Allison JP, et al. Immune-mediated inhibition of metastases after treatment with local radiation and CTLA-4 blockade in a mouse model of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2005) 11:728–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

