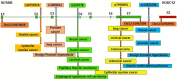
Association Between SNPs of Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR and Risk of Different Cancers
- PMID: 30873206
- PMCID: PMC6403183
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00113
Association Between SNPs of Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR and Risk of Different Cancers
Keywords: HOTAIR; SNP; cancer; lncRNA; polymorphism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Polymorphisms with Cervical Cancer Risk in a Chinese Population.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 28;11(7):e0160039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160039. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27467165 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HOTAIR Polymorphisms Association with Cancer Susceptibility in Different Tumor Types.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(10):1220-1226. doi: 10.2174/1389450118666170622091940. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28641521 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA DRHC inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells in triple negative breast cancer by downregulating long non-coding RNA HOTAIR.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):3817-3822. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10683. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31516593 Free PMC article.
-
A functional lncRNA HOTAIR genetic variant contributes to gastric cancer susceptibility.Mol Carcinog. 2016 Jan;55(1):90-6. doi: 10.1002/mc.22261. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Mol Carcinog. 2016. PMID: 25640751
-
LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Aug;1856(1):151-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26208723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Milk thistle nano-micelle formulation promotes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through modulating miR-155-3p /SOCS2 /PHLDA1 signaling axis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Sep 26;23(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04168-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37749575 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Genetic Polymorphisms in Long Noncoding RNA HOTTIP with Risk of Idiopathic Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion.Biochem Genet. 2024 Aug;62(4):2884-2906. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10571-x. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38038774 Review.
-
Ginsenoside-Rg3 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of hepatoma carcinoma cells via regulating long non-coding RNA HOX antisense intergenic.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):2398-2409. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1932211. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34130594 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-coding RNAs Mechanisms of Action in HIV-1 Modulation and the Identification of Novel Therapeutic Targets.Noncoding RNA. 2020 Mar 13;6(1):12. doi: 10.3390/ncrna6010012. Noncoding RNA. 2020. PMID: 32183241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Novel Lung Cancer Driver Genes Connecting Different Omics Levels With a Heat Diffusion Algorithm.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 26;10:825272. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.825272. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35155435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayram S., Sümbül A. T., Dadaş E. (2016). A functional HOTAIR rs12826786 C> T polymorphism is associated with breast cancer susceptibility and poor clinicopathological characteristics in a Turkish population: a hospital-based case–control study. Tumor Biol. 37, 5577–5584. 10.1007/s13277-015-4430-y - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources