Identification of Key lncRNAs Associated With Atherosclerosis Progression Based on Public Datasets
- PMID: 30873207
- PMCID: PMC6403132
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00123
Identification of Key lncRNAs Associated With Atherosclerosis Progression Based on Public Datasets
Abstract
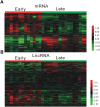
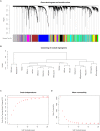
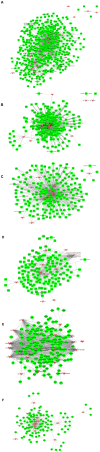
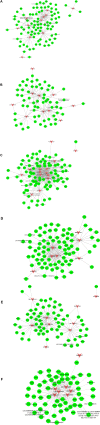
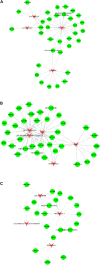
Atherosclerosis is one of the most common type of cardiovascular disease and the prime cause of mortality in the aging population worldwide. However, the detail mechanisms and special biomarkers of atherosclerosis remain to be further investigated. Lately, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) has attracted much more attention than other types of ncRNAs. In our work, we found and confirmed differently expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs in atherosclerosis by analyzing GSE28829. We performed the weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) by analyzing GSE40231 to confirm highly correlated genes. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis were utilized to assess the potential functions of differential expressed lncRNAs in atherosclerosis. Co-expression networks were also constructed to confirm hub lncRNAs in atherosclerosis. A total of 5784 mRNAs and 654 lncRNAs were found to be dysregulated in the progression of atherosclerosis. A total of 15 lncRNA-mRNA co-expression modules were identified in this study based on WGCNA analysis. Moreover, a few lncRNAs, such as ZFAS1, LOC100506730, LOC100506691, DOCK9-AS2, RP11-6I2.3, LOC100130219, were confirmed as important lncRNAs in atherosclerosis. Taken together, bioinformatics analysis revealed these lncRNAs were involved in regulating the leukotriene biosynthetic process, gene expression, actin filament organization, t-circle formation, antigen processing, and presentation, interferon-gamma-mediated signaling pathway, and activation of GTPase activity. We believed that this study would provide potential novel therapeutic and prognostic targets for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: WGCNA analysis; atherosclerosis; biomarker; co-expression analysis; long non-coding RNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulating the Expression of Exercise-induced lncRNAs: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease Progression.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024 Jun 10. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10530-w. Online ahead of print. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38858339 Review.
-
Identification of novel key lncRNAs involved in periodontitis by weighted gene co-expression network analysis.J Periodontal Res. 2020 Jan;55(1):96-106. doi: 10.1111/jre.12693. Epub 2019 Sep 12. J Periodontal Res. 2020. PMID: 31512745
-
Integrative Analysis of Genomics and Transcriptome Data to Identify Regulation Networks in Female Osteoporosis.Front Genet. 2020 Nov 30;11:600097. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.600097. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33329745 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis identified a novel 3-LncRNA regulatory network of transthyretin attenuating glucose induced hRECs dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Oct 15;12(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0596-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31615521 Free PMC article.
-
Screening potential prognostic biomarkers of long non-coding RNAs for predicting the risk of chronic kidney disease.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019 Nov 7;52(11):e8333. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20198333. eCollection 2019. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019. PMID: 31721901 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Crucial Gene Identification in Carotid Atherosclerosis Based on Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Data by Weighted (Gene) Correlation Network Analysis (WGCNA).Med Sci Monit. 2020 Mar 11;26:e921692. doi: 10.12659/MSM.921692. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32160184 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating the Expression of Exercise-induced lncRNAs: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease Progression.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024 Jun 10. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10530-w. Online ahead of print. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38858339 Review.
-
Select Macrophage Noncoding RNAs of Interest in Cardiovascular Disease.J Lipid Atheroscler. 2020 Jan;9(1):153-161. doi: 10.12997/jla.2020.9.1.153. Epub 2020 Jan 16. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2020. PMID: 32821728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retracted Article: LncRNA OIP5-AS1 contributes to ox-LDL-induced inflammation and oxidative stress through regulating the miR-128-3p/CDKN2A axis in macrophages.RSC Adv. 2019 Dec 17;9(71):41709-41719. doi: 10.1039/c9ra08322g. eCollection 2019 Dec 13. RSC Adv. 2019. Retraction in: RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 28;11(9):5241. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90042k. PMID: 35541591 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Analysis of Immune and Inflammation Characteristics of Atherosclerosis from Different Sample Sources.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 25;2022:5491038. doi: 10.1155/2022/5491038. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35509837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding K., Liao Y., Gong D., Zhao X., Ji W. (2018). Effect of long non-coding RNA H19 on oxidative stress and chemotherapy resistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 502 194–201. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.143 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

