Back to the future: Why we need enzymology to build a synthetic metabolism of the future
- PMID: 30873239
- PMCID: PMC6404388
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.15.49
Back to the future: Why we need enzymology to build a synthetic metabolism of the future
Abstract
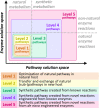
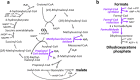
Biology is turning from an analytical into a synthetic discipline. This is especially apparent in the field of metabolic engineering, where the concept of synthetic metabolism has been recently developed. Compared to classical metabolic engineering efforts, synthetic metabolism aims at creating novel metabolic networks in a rational fashion from bottom-up. However, while the theoretical design of synthetic metabolic networks has made tremendous progress, the actual realization of such synthetic pathways is still lacking behind. This is mostly because of our limitations in enzyme discovery and engineering to provide the parts required to build synthetic metabolism. Here I discuss the current challenges and limitations in synthetic metabolic engineering and elucidate how modern day enzymology can help to build a synthetic metabolism of the future.
Keywords: enzymes; in vitro biochemistry; metabolic engineering; synthetic biology.
Figures
References
-
- Jaffe B. Crucibles: The Story of Chemistry from Ancient Alchemy to Nuclear Fission. New York: Dover Publications; 1976.
-
- Wöhler F. Ann Phys (Berlin, Ger) 1828;88:253–256. doi: 10.1002/andp.18280870206. - DOI
-
- Asimov I A. Short History of Chemistry. Garden City, New York: Anchor Books; 1967.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
