Diagnostic Significance of Serum IgG Galactosylation in CA19-9-Negative Pancreatic Carcinoma Patients
- PMID: 30873386
- PMCID: PMC6402387
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00114
Diagnostic Significance of Serum IgG Galactosylation in CA19-9-Negative Pancreatic Carcinoma Patients
Abstract
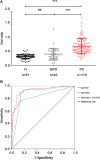
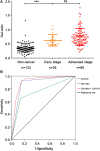
Background: Although Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) is considered clinically useful and informative for pancreatic carcinoma (PC), false positive results, and false negative results have restricted its clinical use. Especially missed or delayed diagnosis of PC patients with negative CA19-9 value limited the utility. To improve prognosis of PC patients, the discovery of reliable biomarkers to assist CA19-9 is desired. Serum IgG galactosylation based on our previous report was altered in PC patients comparing to healthy controls. The objective of this study was to explore the diagnostic significance of IgG galactosylation in assisting CA19-9 for PC in a comprehensive way. Methods: Serum IgG galactosylation profiles were analyzed by MALDI-MS in cohort 1 (n = 252) and cohort 2 in which all CA19-9 levels were negative (n = 133). In each cohort, not only healthy controls and PC patients but also benign pancreatic disease (BPD) patients were enrolled. Peaks were acquired by the software of MALDI-MS sample acquisition, followed by being processed and analyzed by the software of Progenesis MALDI. IgG Gal-ratio, which was calculated from the relative intensity of peaks G0, G1, and G2 according to the formula (G0/(G1+G2×2)), was employed as an index for indicating the distribution of IgG galactosylation. Results: The Gal-ratio was elevated in PC comparing with that in non-cancer group (healthy controls and BPD). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of IgG Gal-ratio was higher than that of CA19-9 (0.912 vs. 0.814). The performance was further improved when Gal-ratio and CA19-9 were combined (AUC: 0.928). Meanwhile, Gal-ratio also had great diagnostic value with a sensitivity of 92.31% (AUC: 0.883) in detection of PC at early stage. Notably, IgG Gal-ratio has great sensitivity (90.63%) and specificity (76.81%) in CA19-9-negative PC patients. Conclusions: IgG Gal-ratio had a great performance in detection of PC and could be used to assist CA19-9 in improving diagnosis performance through early stage detection, differentiation from BPD, and PC diagnosis with CA19-9-negative level.
Keywords: CA19-9; IgG; diagnostic biomarker; galactosylation; pancreatic carcinoma.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

