The role of TNF-α in rheumatoid arthritis: a focus on regulatory T cells
- PMID: 30873466
- PMCID: PMC6410649
The role of TNF-α in rheumatoid arthritis: a focus on regulatory T cells
Abstract
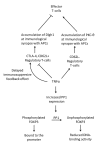
The autoimmune disorder rheumatoid arthritis (RA) causes chronic inflammation and destruction of joints. T cells are a predominant component of the synovial environment in RA, however the functional role of these cells is not yet fully understood. This is in part due to the fact that the balance and importance of the relation of Tregs with T-effector cells in RA is still under investigation. The current treatment regimen for this debilitating disease focuses on controlling symptoms and preventing further joint damage through the use of therapies which affect different areas of the immune system at the synovium. One of the main therapies involves Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors. In the RA immune-environment, TNF-α has been shown to have an influential and extensive but as yet poorly understood effect on Treg function in vivo, and undoubtably an important role in the treatment of RA. Interestingly, the high levels of TNF-α found in RA patients appear to interfere with the mechanisms controlling the suppressive function of Tregs. Relevance for patients: This review focuses on the conflicting literature available regarding the role played by Tregs in RA and the impact of TNF-α and anti-TNF-α therapies on Tregs in this scenario. Individuals suffering from RA can benefit from better insight of the treatment mechanisms of the immunologic processes which occur throughout this disease, as current treatments for RA focus on several different areas of the immune system at the synovial compartment.
Keywords: TNF-α therapy; joint inflammation; regulatory T cells; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham III CO, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VR, Cohen MC, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery R, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JMW, Hobbs K, Huizinga TWJ, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Ménard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PR, Upchurch KS, Vencovský J, Wolfe F, Hawker G. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205–2219. - PubMed
-
- Cimmino MA, Zampogna A, Murroni S, Baruffi S, Alessio G, Maio T, Mela GS. Methodology of an epidemiologic prevalence study in rheumatology: the Chiavari study. Reumatismo. 2002;54:40–47. - PubMed
-
- Aho K, Kaipaiainen-Seppanen O, Helovaara M, Klaukka T. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis in Finland. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1998;27:325–334. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
