Higher order genomic organization and epigenetic control maintain cellular identity and prevent breast cancer
- PMID: 30873710
- PMCID: PMC6549233
- DOI: 10.1002/gcc.22731
Higher order genomic organization and epigenetic control maintain cellular identity and prevent breast cancer
Abstract
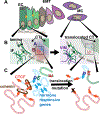
Cells establish and sustain structural and functional integrity of the genome to support cellular identity and prevent malignant transformation. In this review, we present a strategic overview of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms including histone modifications and higher order chromatin organization (HCO) that are perturbed in breast cancer onset and progression. Implications for dysfunctions that occur in hormone regulation, cell cycle control, and mitotic bookmarking in breast cancer are considered, with an emphasis on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell activities. The architectural organization of regulatory machinery is addressed within the contexts of translating cancer-compromised genomic organization to advances in breast cancer risk assessment, diagnosis, prognosis, and identification of novel therapeutic targets with high specificity and minimal off target effects.
Keywords: RUNX; breast cancer; cancer stem cells; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; higher order chromatin organization; hormone regulation; mitotic bookmarking.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
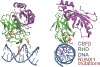

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01GM129338/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129338/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA220935/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54CA217297/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DE012528/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA230618/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI055402/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32CA236125/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM118228/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA082834/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM129338/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32 CA220935/BC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DE012528/BC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA196383/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA139322/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DE012528/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

