Advanced Micro- and Nano-Gas Sensor Technology: A Review
- PMID: 30875734
- PMCID: PMC6470538
- DOI: 10.3390/s19061285
Advanced Micro- and Nano-Gas Sensor Technology: A Review
Abstract
Micro- and nano-sensors lie at the heart of critical innovation in fields ranging from medical to environmental sciences. In recent years, there has been a significant improvement in sensor design along with the advances in micro- and nano-fabrication technology and the use of newly designed materials, leading to the development of high-performance gas sensors. Advanced micro- and nano-fabrication technology enables miniaturization of these sensors into micro-sized gas sensor arrays while maintaining the sensing performance. These capabilities facilitate the development of miniaturized integrated gas sensor arrays that enhance both sensor sensitivity and selectivity towards various analytes. In the past, several micro- and nano-gas sensors have been proposed and investigated where each type of sensor exhibits various advantages and limitations in sensing resolution, operating power, response, and recovery time. This paper presents an overview of the recent progress made in a wide range of gas-sensing technology. The sensing functionalizing materials, the advanced micro-machining fabrication methods, as well as their constraints on the sensor design, are discussed. The sensors' working mechanisms and their structures and configurations are reviewed. Finally, the future development outlook and the potential applications made feasible by each category of the sensors are discussed.
Keywords: acoustic gas sensors; carbon nano-tube (CNT) Sensors; electrochemical gas sensors; fiber-optic gas sensors; metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) sensors; micro-electro mechanical systems (MEMS); organic-based chemiresistive gas sensors; photonic crystal gas sensors; piezoelectric gas sensors; volatile organic compound (VOC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


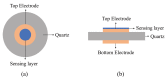
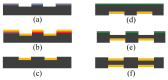
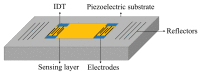

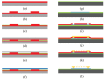

References
-
- Seiyama T., Kagawa S. Study on a Detector for Gaseous Components Using Semiconductive Thin Films. Anal. Chem. 1966;38:1069–1073. doi: 10.1021/ac60240a031. - DOI
-
- Refaat T.F., Ismail S., Koch G.J., Rubio M., Mack T.L., Notari A., Collins J.E., Lewis J., De Young R., Choi Y., et al. Backscatter 2-μm Lidar Validation for Atomospheric CO2 Differential Absorption Lidar Applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011;49:572–580. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2055874. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

