A Vortex-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by UPLC-MS/MS for Simultaneous Determination of Pesticides and Aflatoxins in Herbal Tea
- PMID: 30875921
- PMCID: PMC6472212
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24061029
A Vortex-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Followed by UPLC-MS/MS for Simultaneous Determination of Pesticides and Aflatoxins in Herbal Tea
Abstract
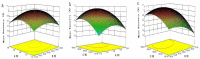
A method for detecting the organophosphorus pesticides residue and aflatoxins in China herbal tea has been developed by UPLC-MS/MS coupled with vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME). The extraction conditions for vortex-assisted DLLME extraction were optimized using single-factor experiments and response surface design. The optimum conditions for the experiment were the pH 5.1, 347 µL of chloroform (extraction solvent) and 1614 µL of acetonitrile (dispersive solvent). Under the optimum conditions, the targets were good linearity in the range of 0.1 µg/L⁻25 µg/L and the correlation coefficient above 0.9998. The mean recoveries of all analytes were in the ranged from 70.06%⁻115.65% with RSDs below 8.54%. The detection limits were in the range of 0.001 µg/L⁻0.01µg/L. The proposed method is a fast and effective sample preparation with good enrichment and extraction efficiency, which can simultaneously detect pesticides and aflatoxins in China herbal tea.
Keywords: China herbal tea; UPLC-MS/MS; aflatoxins; pesticides residue; vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Determination of pyrethroid residues in herbal tea using temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by high performance liquid chromatography.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 13;10(1):4709. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61755-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32170197 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of the one-step purification method coupled to LC-MS/MS for simultaneous determination of four aflatoxins in fermented tea.Food Chem. 2021 Aug 30;354:129497. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129497. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33752112
-
Vortex-assisted low density solvent based demulsified dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water samples.Chemosphere. 2014 May;103:51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.024. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Chemosphere. 2014. PMID: 24332733
-
Multi-residue method for determination of 58 pesticides, pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water using solvent demulsification dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.Talanta. 2016 Jan 1;146:676-88. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.06.047. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Talanta. 2016. PMID: 26695317
-
Green aspects, developments and perspectives of liquid phase microextraction techniques.Talanta. 2014 Feb;119:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.10.050. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Talanta. 2014. PMID: 24401382 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Dealcoholization by Osmotic Distillation on Metabolic Profile, Phenolic Content, and Antioxidant Capacity of Low Alcoholic Craft Beers with Different Malt Compositions.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Apr 28;69(16):4816-4826. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c00679. Epub 2021 Apr 15. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33855852 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical Sensing Platform Based on Carbon Dots for the Simultaneous Determination of Theophylline and Caffeine in Tea.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 7;23(18):7731. doi: 10.3390/s23187731. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765788 Free PMC article.
-
Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction (DLLME) and LC-MS/MS Analysis for Multi-Mycotoxin in Rice Bran: Method Development, Optimization and Validation.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 15;13(4):280. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040280. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920815 Free PMC article.
-
A New Benzaldehyde Derivative Exhibits Antiaflatoxigenic Activity against Aspergillus flavus.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Nov 12;9(11):1103. doi: 10.3390/jof9111103. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998908 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization and Validation of Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction for Simultaneous Determination of Aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, and G2 in Senna Leaves and Pods Using HPLC-FLD with Pre-Column Derivatization.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;15(4):277. doi: 10.3390/toxins15040277. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37104215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin B., Liu Y., Xie J., Luo B., Long C. Ethnobotanical survey of plant species for herbal tea in a Yao autonomous county (Jianghua, China): Results of a 2-year study of traditional medicinal markets on the Dragon Boat Festival. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2018;14:58–78. doi: 10.1186/s13002-018-0257-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Han B.Q., Peng Y., Xiao P.G. Systematic Research on Chinese Non-Camellia Tea. Mod. Chin. Med. 2013;15:259–269.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

