Survival outcomes after whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases in older adults with newly diagnosed metastatic small cell carcinoma: A national cancer database (NCDB) analysis
- PMID: 30876834
- PMCID: PMC7425589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgo.2019.01.017
Survival outcomes after whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases in older adults with newly diagnosed metastatic small cell carcinoma: A national cancer database (NCDB) analysis
Abstract
Background: Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive malignancy with a tendency to affect older adults and also metastasize to the brain. Older adults tolerate whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) poorly with marginal survival benefit. We utilized the national cancer database (NCDB) to evaluate the survival outcomes following WBRT in older adults with SCLC and brain metastases.
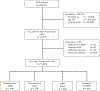
Methods: We identified 1615 patients ≥75 years old diagnosed with SCLC and brain metastases. Patients were categorized by type of therapy: chemotherapy + WBRT (n = 576), chemotherapy alone (n = 238), WBRT alone (n = 360) and no chemotherapy or WBRT (n = 441). Clinical and demographic characteristics were reported for each treatment cohort with a subsequent multivariable regression analysis for survival.
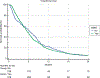
Results: Median patient age was 79 years. WBRT median dose was 30 Gy. At time of analysis, 1530 of the cohort had died, yielding a median OS of 2.9 months and 6 month survival of 31% for patients that received chemotherapy. For patients treated without chemotherapy, median OS with WBRT was 1.9 months compared to 1.2 months without (p < .0001). For patients receiving chemotherapy with, and without WBRT, median OS was 5.6 months and 6.4 months, respectively (p = .43). Multivariable cox regression revealed age > 80, extracranial disease, male sex, and rural location as predictors of increased risk of death.
Conclusion: In older adult patients with SCLC brain metastasis, WBRT was associated with a modest increase in survival in patients not fit for chemotherapy, and there was no association with increased survival over chemotherapy alone.
Keywords: Brain metastases; Elderly; Small cell lung cancer; Whole brain radiation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiosurgery alone is associated with favorable outcomes for brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2018 Jun;120:88-90. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.03.027. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29748022
-
Outcome and prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer treated with whole brain radiotherapy.J Neurooncol. 2017 Aug;134(1):205-212. doi: 10.1007/s11060-017-2510-0. Epub 2017 May 30. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 28560661
-
Efficacy and limitations of salvage gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases of small-cell lung cancer after whole-brain radiotherapy.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013 Jan;155(1):107-13; discussion 113-4. doi: 10.1007/s00701-012-1520-0. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013. PMID: 23065044
-
Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on the Role of Whole Brain Radiation Therapy in Adults With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Brain Tumors.Neurosurgery. 2019 Mar 1;84(3):E159-E162. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy541. Neurosurgery. 2019. PMID: 30629211
-
A systematic approach to the management of patients with brain metastases of known or unknown primary site.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;69(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1775-9. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22042515 Review.
Cited by
-
Third-line or above anlotinib in relapsed and refractory small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A post hoc analysis of ALTER1202, a randomized, double-blind phase 2 study.Cancer Innov. 2023 Jan 17;2(3):181-190. doi: 10.1002/cai2.43. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cancer Innov. 2023. PMID: 38089404 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty-Month Regression Following Concurrent Conventional Whole-Brain Irradiation and Chemoimmunotherapy for ≥3.8 cm Cerebellar Metastasis From Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cureus. 2023 Aug 19;15(8):e43759. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43759. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37727186 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate Irradiation Induced Cerebral Water and Hemodynamic Response in Whole Brain Radiotherapy.Ann Biomed Eng. 2025 Mar;53(3):673-682. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03663-1. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Ann Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 39633157 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 inhibitors combined with whole brain radiotherapy in patients with small cell lung cancer brain metastases: Real-world evidence.Cancer Med. 2024 Apr;13(7):e7125. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7125. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38613182 Free PMC article.
-
Management of brain metastases in elderly patients with lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2021 May;13(5):3295-3307. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2019-rbmlc-05. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 34164222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cancer statistics review, 1975–2015 - SEER statistics. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/. Accessed May 3, 2018, 2018.
-
- Quan AL, Videtic GMM, Suh JH. Brain metastases in small cell lung cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2004;18(8) 961-72, 979–980, 987 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15328892, Accessed date: 3 May 2018. - PubMed
-
- Sirzén F, Zhivotovsky B, Nilsson A, Bergh J, Lewensohn R. Spontaneous and radiation-induced apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells with different intrinsic radio-sensitivities. Anticancer Res 2018;18(2A):695–9, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9615707, Accessed date: 3 May 2018. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

