Transposition of IS 4 Family Insertion Sequences IS Teha3, IS Teha4, and IS Teha5 into the arc Operon Disrupts Arginine Deiminase System in Tetragenococcus halophilus
- PMID: 30877114
- PMCID: PMC6498170
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00208-19
Transposition of IS 4 Family Insertion Sequences IS Teha3, IS Teha4, and IS Teha5 into the arc Operon Disrupts Arginine Deiminase System in Tetragenococcus halophilus
Abstract
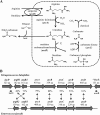
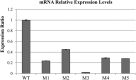
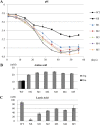
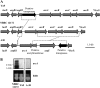
Tetragenococcus halophilus, a halophilic lactic acid bacterium, is often used as a starter culture in the manufacturing of soy sauce. T. halophilus possesses an arginine deiminase system, which is responsible for the accumulation of citrulline, the main precursor of the potential carcinogen ethyl carbamate. In this study, we generated five derivatives lacking arginine deiminase activity from T. halophilus NBRC 12172 by UV irradiation. Using these derivatives as a fermentation starter prevented arginine deimination in soy sauce. DNA sequence analysis of the derivatives revealed that novel IS4 family insertion sequences, designated ISTeha3, ISTeha4, and ISTeha5, were transposed into the region around the arginine deiminase (arc) operon in the mutants. These insertion sequences contain a single open reading frame encoding a putative transposase and 13- to 15-bp inverted repeats at both termini, which are adjacent to 7- to 9-bp duplications of the target sequence. Investigation of wild strains isolated from soy sauce mash incapable of arginine deimination also indicated that insertion sequences are involved in the disruption of the arginine deiminase system in T. halophilusIMPORTANCE Insertion sequences play important roles in bacterial evolution and are frequently utilized in mutagenesis systems. However, the intrinsic insertion sequences of tetragenococci are not well characterized. Here, we identified three active insertion sequences of T. halophilus by transposition into the region around the arc operon. This report provides an example of insertion sequence-mediated generation and evolution of T. halophilus and primary information about their characteristics.
Keywords: Tetragenococcus halophilus; arginine deiminase system; ethyl carbamate; insertion sequence.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of an operon and its regulator required for autoaggregation in Tetragenococcus halophilus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Dec 21;89(12):e0145823. doi: 10.1128/aem.01458-23. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38014957 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of arginine deiminase system-deficient mutants of Tetragenococcus halophilus using arginine analog canavanine.J Biosci Bioeng. 2024 Oct;138(4):324-327. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2024.07.006. Epub 2024 Jul 29. J Biosci Bioeng. 2024. PMID: 39079833
-
Targeted Screening for Spontaneous Insertion Mutations in a Lactic Acid Bacterium, Tetragenococcus halophilus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Mar 29;89(3):e0200522. doi: 10.1128/aem.02005-22. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36809065 Free PMC article.
-
Co-culture with Tetragenococcus halophilus improved the ethanol tolerance of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii by maintaining cell surface properties.Food Microbiol. 2021 Aug;97:103750. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2021.103750. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Food Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33653523 Review.
-
Formation of biofilm changed the responses of Tetragenococcus halophilus to ethanol stress revealed by transcriptomic and proteomic analyses.Food Res Int. 2022 Nov;161:111817. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111817. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36192889 Review.
Cited by
-
The diversity among the species Tetragenococcus halophilus including new isolates from a lupine seed fermentation.BMC Microbiol. 2021 Nov 20;21(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02381-1. BMC Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34798831 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of Closely Related Tetragenococcus halophilus Strains Elucidate the Diversity and Microevolution of CRISPR Elements.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 18;12:687985. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.687985. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34220781 Free PMC article.
-
Ribitol-Containing Wall Teichoic Acid of Tetragenococcus halophilus Is Targeted by Bacteriophage phiWJ7 as a Binding Receptor.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0033622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00336-22. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35311554 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin and proper phospholipid composition are important for aggregation in Tetragenococcus halophilus SL10.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 May 21;90(5):e0033424. doi: 10.1128/aem.00334-24. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38624197 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an operon and its regulator required for autoaggregation in Tetragenococcus halophilus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Dec 21;89(12):e0145823. doi: 10.1128/aem.01458-23. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38014957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baliga NS, Bonneau R, Facciotti MT, Pan M, Glusman G, Deutsch EW, Shannon P, Chiu Y, Weng RS, Gan RR, Hung P, Date SV, Marcotte E, Hood L, Ng WV. 2004. Genome sequence of Haloarcula marismortui: a halophilic archaeon from the Dead Sea. Genome Res 14:2221–2234. doi:10.1101/gr.2700304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blattner FR, Plunkett G, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, Gregor J, Davis NW, Kirkpatrick HA, Goeden MA, Rose DJ, Mau B, Shao Y. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453–1462. doi:10.1126/science.277.5331.1453. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

