Dependence on Myb expression is attenuated in myeloid leukaemia with N-terminal CEBPA mutations
- PMID: 30877232
- PMCID: PMC6421631
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.201800207
Dependence on Myb expression is attenuated in myeloid leukaemia with N-terminal CEBPA mutations
Abstract
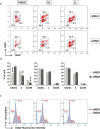
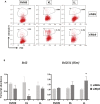
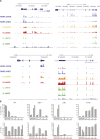
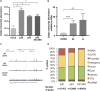
Mutations at the N- or C-terminus of C/EBPα are frequent in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) with normal karyotype. Here, we investigate the role of the transcription factor Myb in AMLs driven by different combinations of CEBPA mutations. Using knockdown of Myb in murine cell lines modelling the spectrum of CEBPA mutations, we show that the effect of reduced Myb depends on the mutational status of the two Cebpa alleles. Importantly, Myb knockdown fails to override the block in myeloid differentiation in cells with biallelic N-terminal C/EBPα mutations, demonstrating for the first time that the dependency on Myb is much lower in AML with this mutational profile. By comparing gene expression following Myb knockdown and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing data for the binding of C/EBPα isoforms, we provide evidence for a functional cooperation between C/EBPα and Myb in the maintenance of AML. This co-dependency breaks down when both alleles of CEBPA harbour N-terminal mutations, as a subset of C/EBPα-regulated genes only bind the short p30 C/EBPα isoform and, unlike other C/EBPα-regulated genes, do so without a requirement for Myb.
© 2019 Volpe et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bereshchenko O, Mancini E, Moore S, Bilbao D, Mansson R, Luc S, Grover A, Jacobsen SE, Bryder D, Nerlov C (2009) Hematopoietic stem cell expansion precedes the generation of committed myeloid leukemia-initiating cells in C/EBPalpha mutant AML. Cancer Cell 16: 390–400. 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.09.036 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
