ALS/FTD mutant CHCHD10 mice reveal a tissue-specific toxic gain-of-function and mitochondrial stress response
- PMID: 30877432
- PMCID: PMC6571048
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-019-01989-y
ALS/FTD mutant CHCHD10 mice reveal a tissue-specific toxic gain-of-function and mitochondrial stress response
Abstract
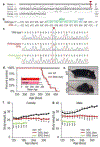
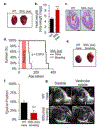
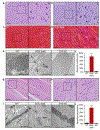
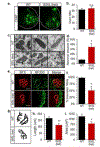
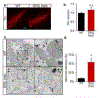
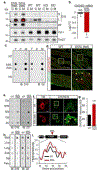
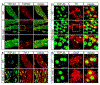
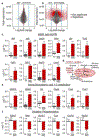
Mutations in coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 10 (CHCHD10), a mitochondrial protein of unknown function, cause a disease spectrum with clinical features of motor neuron disease, dementia, myopathy and cardiomyopathy. To investigate the pathogenic mechanisms of CHCHD10, we generated mutant knock-in mice harboring the mouse-equivalent of a disease-associated human S59L mutation, S55L in the endogenous mouse gene. CHCHD10S55L mice develop progressive motor deficits, myopathy, cardiomyopathy and accelerated mortality. Critically, CHCHD10 accumulates in aggregates with its paralog CHCHD2 specifically in affected tissues of CHCHD10S55L mice, leading to aberrant organelle morphology and function. Aggregates induce a potent mitochondrial integrated stress response (mtISR) through mTORC1 activation, with elevation of stress-induced transcription factors, secretion of myokines, upregulated serine and one-carbon metabolism, and downregulation of respiratory chain enzymes. Conversely, CHCHD10 ablation does not induce disease pathology or activate the mtISR, indicating that CHCHD10S55L-dependent disease pathology is not caused by loss-of-function. Overall, CHCHD10S55L mice recapitulate crucial aspects of human disease and reveal a novel toxic gain-of-function mechanism through maladaptive mtISR and metabolic dysregulation.
Keywords: ALS; CHCHD10; CHCHD2; FTD; Knock-in mice; Mitochondrial integrated stress response; Mitochondrial myopathy; Neurodegeneration; Protein aggregation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bannwarth S, Ait-El-Mkadem S, Chaussenot A, Genin EC, Lacas-Gervais S, Fragaki K, Berg-Alonso L, Kageyama Y, Serre V, Moore DG et al. (2014) A mitochondrial origin for frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis through CHCHD10 involvement. Brain 137: 2329–2345 Doi 10.1093/brain/awu138 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burstein SR, Valsecchi F, Kawamata H, Bourens M, Zeng R, Zuberi A, Milner TA, Cloonan SM, Lutz C, Barrientos A et al. (2018) In vitro and in vivo studies of the ALS-FTLD protein CHCHD10 reveal novel mitochondrial topology and protein interactions. Hum Mol Genet 27: 160–177 Doi 10.1093/hmg/ddx397 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

