Comparing duloxetine and pregabalin for treatment of pain and depression in women with fibromyalgia: an open-label randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 30877484
- PMCID: PMC6593027
- DOI: 10.1007/s40199-019-00257-4
Comparing duloxetine and pregabalin for treatment of pain and depression in women with fibromyalgia: an open-label randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Duloxetine and pregabalin are among the most widely used medications in the treatment of patients with fibromyalgia syndrome (FM).
Objectives: To add to the very few lines of evidence that exist on the comparative safety and efficacy of these two medications.
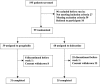
Methods: In this open-label randomized clinical trial, outpatient women, who were diagnosed with FM based on American College of Rheumatology 2010 criteria, and had an age range of 18-65 years old were assigned to either duloxetine 30-60 mg or pregabalin 75-150 mg per day for 4 weeks. Patients were excluded in cases of having used duloxetine, pregabalin, gabapentin, or antidepressants within 12 weeks prior to the study, having had a history of comorbid medical conditions that could provoke chronic pain, or having had comorbid neuropsychiatric disorders, except for major depressive/anxiety disorders. Primary outcomes were between-group differences in mean score changes from baseline to end point for Widespread Pain Index (WPI) and Beck Depression Inventory-II. Secondary outcomes were the same statistical estimates, but for Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire-Revised and 12-Item Short Form Survey. Descriptive statistics and independent samples t-test were the main methods of analysis. ( www.irct.ir ; IRCT2016030626935N1).
Results: Among all the scales, only WPI scores improved with a statistically significant difference between the two treatment arms, favoring duloxetine (Mean difference in score change - 2.32, 95% CI, -4.46 to - 0.18; p = 0.034; Cohen's d 0.53 95% CI, 0.04 to 1.02). Drop out rate and cumulative incidence of nausea was significantly higher in the duloxetine arm compared to the pregabalin arm.
Conclusion: This study provides further evidence on higher efficacy of duloxetine compared to pregabalin for the treatment of pain in patients with fibromyalgia. Future comprehensive pragmatic clinical trials are warranted.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Duloxetine; Fibromyalgia; Pregabalin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yunus MB, Inanici F, Aldag JC, Mangold RF. Fibromyalgia in men: comparison of clinical features with women. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(2):485–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical