Matrix metalloproteinase-7 protects against acute kidney injury by priming renal tubules for survival and regeneration
- PMID: 30878215
- PMCID: PMC6478554
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.11.043
Matrix metalloproteinase-7 protects against acute kidney injury by priming renal tubules for survival and regeneration
Abstract
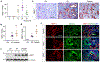
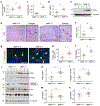
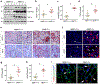
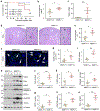
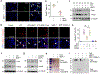
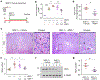
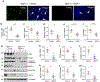
Matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) is a secreted endopeptidase that degrades a broad range of substrates. Recent studies have identified MMP-7 as an early biomarker to predict severe acute kidney injury (AKI) and poor outcomes after cardiac surgery; however, the role of MMP-7 in the pathogenesis of AKI is unknown. In this study, we investigated the expression of MMP-7 and the impact of MMP-7 deficiency in several models of AKI. MMP-7 was induced in renal tubules following ischemia/ reperfusion injury or cisplatin administration, and in folic acid-induced AKI. MMP-7 knockout mice experienced higher mortality, elevated serum creatinine, and more severe histologic lesions after ischemic or toxic insults. Tubular apoptosis and interstitial inflammation were more prominent in MMP-7 knockout kidneys. These histologic changes were accompanied by increased expression of FasL and other components of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, as well as increased expression of pro-inflammatory chemokines. In a rescue experiment, exogenous MMP-7 ameliorated kidney injury in MMP-7 knockout mice after ischemia/reperfusion. In vitro, MMP-7 protected tubular epithelial cells against apoptosis by directly degrading FasL. In isolated tubules ex vivo, MMP-7 promoted cell proliferation by degrading E-cadherin and thereby liberating β-catenin, priming renal tubules for regeneration. Taken together, these results suggest that induction of MMP-7 is protective in AKI by degrading FasL and mobilizing β-catenin, thereby priming kidney tubules for survival and regeneration.
Keywords: FasL; MMP-7; acute kidney injury; apoptosis; proliferation; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2019 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tubule-specific ablation of endogenous β-catenin aggravates acute kidney injury in mice.Kidney Int. 2012 Sep;82(5):537-47. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.173. Epub 2012 May 23. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22622501 Free PMC article.
-
Role of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in recovery after tubular damage in acute kidney injury in mice.Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2012;122(1-2):23-35. doi: 10.1159/000346569. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 23548779
-
Activation of hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-met, in renal tubules is required for renoprotection after acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2013 Sep;84(3):509-20. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.102. Epub 2013 May 29. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23715119 Free PMC article.
-
The Many Faces of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Kidney Diseases.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 25;10(6):960. doi: 10.3390/biom10060960. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32630493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Signaling in Acute Kidney Injury.Nephron. 2020;144(12):609-612. doi: 10.1159/000509354. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Nephron. 2020. PMID: 32726778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renogrit attenuates Vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in human renal spheroids and in Sprague-Dawley rats by regulating kidney injury biomarkers and creatinine/urea clearance.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 8;18(11):e0293605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293605. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37939153 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Damage in Long COVID: Studies in Experimental Mice.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jul 30;12(8):1070. doi: 10.3390/biology12081070. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37626956 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary matrix metalloproteinase-7 is a sensitive biomarker to evaluate renal tubular injury in patients with minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Feb 10;17(1):sfad027. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad027. eCollection 2024 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38186883 Free PMC article.
-
Urine MMP7 as a kidney injury biomarker.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Sep 14;17(1):sfad233. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad233. eCollection 2024 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38186894 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM10 and ADAM17, Major Regulators of Chronic Kidney Disease Induced Atherosclerosis?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 15;24(8):7309. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087309. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sharfuddin AA, Molitoris BA. Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol 2011;7:189–200. - PubMed
-
- Rewa O, Bagshaw SM. Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat Rev Nephrol 2014;10:193–207. - PubMed
-
- Singbartl K, Kellum JA. AKI in the ICU: definition, epidemiology, risk stratification, and outcomes. Kidney Int 2012;81:819–825. - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Wald R. Acute kidney injury: Timing of renal replacement therapy in AKI. Nat Rev Nephrol 2016;12:445–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

