miRNA-223 at the crossroads of inflammation and cancer
- PMID: 30878527
- PMCID: PMC6441621
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.02.051
miRNA-223 at the crossroads of inflammation and cancer
Abstract
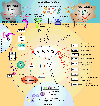
miR-223 is an evolutionarily conserved anti-inflammatory microRNA primarily expressed in myeloid cells. miR-223 post-transcriptionally regulates many genes essential in inflammation, cell proliferation, and invasion. Recent studies show that miR-223 is either endogenously expressed or transferred in exosomes or extracellular vesicles to non-phagocytic cells including cancer cells, where it exerts biological functions. In cancerous cells, miR-223 acts either as an oncomiR promoting tumors or as a tumor suppressor in a context-dependent manner. Taken together, miR-223 can regulate tumorigenesis at multiple levels, including by suppressing the inflammatory tumor microenvironment and modulating malignancy of cancer cells.
Keywords: Macrophages; NF-κB; Neutrophils; OncomiR; Tumor suppressor; microRNA.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Roberto VP, Tiago DM, Gautvik K, Cancela ML, Evidence for the conservation of miR-223 in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Implications for function, Gene, 566 (2015) 54–62. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Liang Y, Han H, Qin H, Identification of a miRNA signature in neutrophils after traumatic injury, Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica, 45 (2013) 938–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

