Acute Effects of Heat-Not-Burn, Electronic Vaping, and Traditional Tobacco Combustion Cigarettes: The Sapienza University of Rome-Vascular Assessment of Proatherosclerotic Effects of Smoking ( SUR - VAPES ) 2 Randomized Trial
- PMID: 30879375
- PMCID: PMC6475061
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010455
Acute Effects of Heat-Not-Burn, Electronic Vaping, and Traditional Tobacco Combustion Cigarettes: The Sapienza University of Rome-Vascular Assessment of Proatherosclerotic Effects of Smoking ( SUR - VAPES ) 2 Randomized Trial
Abstract
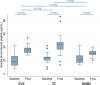
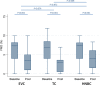
Background Little clinical research on new-generation heat-not-burn cigarettes ( HNBC ) in comparison with electronic vaping cigarettes ( EVC ) and traditional tobacco combustion cigarettes ( TC ) has been reported. We aimed to appraise the acute effects of single use of HNBC , EVC, and TC in healthy smokers. Methods and Results This was an independent, cross-over, randomized trial in 20 TC smokers, with allocation to different cycles of HNBC , EVC , and TC . All participants used all types of products, with an intercycle washout of 1 week. End points were oxidative stress, antioxidant reserve, platelet activation, flow-mediated dilation, blood pressure, and satisfaction scores. Single use of any product led to an adverse impact on oxidative stress, antioxidant reserve, platelet function, flow-mediated dilation, and blood pressure. HNBC had less impact than EVC and TC on soluble Nox2-derived peptide (respectively, P=0.004 and 0.001), 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α- III ( P=0.004 and <0.001), and vitamin E ( P=0.018 and 0.044). HNBC and EVC were equally less impactful than TCs on flow-mediated dilation ( P=0.872 for HNBC versus EVC ), H2O2 ( P=0.522), H2O2 breakdown activity ( P=0.091), soluble CD 40 ligand ( P=0.849), and soluble P-selectin ( P=0.821). The effect of HNBC and, to a lesser extent EVC , on blood pressure was less evident than that of TC , whereas HNBC appeared more satisfying than EVC (all P<0.05). Conclusions Acute effects of HNBC , EVC, and TC are different on several oxidative stress, antioxidant reserve, platelet function, cardiovascular, and satisfaction dimensions, with TCs showing the most detrimental changes in clinically relevant features. Clinical Trial Registration URL : http://www.clinicaltrials.gov . Unique identifier: NCT 03301129.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03301129.
Keywords: flow‐induced dilation; oxidative stress; platelet; platelet aggregation; smoking.
Figures
References
-
- Stallones RA. The association between tobacco smoking and coronary heart disease. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44:735–743. - PubMed
-
- Carnevale R, Loffredo L, Pignatelli P, Nocella C, Bartimoccia S, Di Santo S, Martino F, Catasca E, Perri L, Violi F. Dark chocolate inhibits platelet isoprostanes via NOX2 down‐regulation in smokers. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Loffredo L, Carnevale R, Perri L, Catasca E, Augelletti T, Cangemi R, Albanese F, Piccheri C, Nocella C, Pignatelli P, Violi F. NOX2‐mediated arterial dysfunction in smokers: acute effect of dark chocolate. Heart. 2011;97:1776–1781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

