Olaparib and α-specific PI3K inhibitor alpelisib for patients with epithelial ovarian cancer: a dose-escalation and dose-expansion phase 1b trial
- PMID: 30880072
- PMCID: PMC7025391
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30905-7
Olaparib and α-specific PI3K inhibitor alpelisib for patients with epithelial ovarian cancer: a dose-escalation and dose-expansion phase 1b trial
Abstract
Background: Based on preclinical work, we found that combination of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors with drugs that inhibit the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway (such as PI3K inhibitors) might sensitise HRR-proficient epithelial ovarian cancers to PARP inhibitors. We aimed to assess the safety and identify the recommended phase 2 dose of the PARP inhibitor olaparib in combination with the PI3K inhibitor alpelisib in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer and in patients with breast cancer.
Methods: In this multicentre, open-label, phase 1b trial following a 3 + 3 dose-escalation design, we recruited patients aged 18 years or older with the following key eligibility criteria: confirmed diagnosis of either recurrent ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer of high-grade serous histology; confirmed diagnosis of either recurrent ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer of any histology with known germline BRCA mutations; confirmed diagnosis of recurrent breast cancer of triple-negative histology; or confirmed diagnosis of recurrent breast cancer of any histology with known germline BRCA mutations. Additional patients with epithelial ovarian cancer were enrolled in a dose-expansion cohort. Four dose levels were planned: the starting dose level of alpelisib 250 mg once a day plus olaparib 100 mg twice a day (dose level 0); alpelisib 250 mg once a day plus olaparib 200 mg twice a day (dose level 1); alpelisib 300 mg once a day plus olaparib 200 mg twice a day (dose level 2); and alpelisib 200 mg once a day plus olaparib 200 mg twice a day (dose level 3). Both drugs were administered orally, in tablet formulation. The primary objective was to identify the maximum tolerated dose and the recommended phase 2 dose of the combination of alpelisib and olaparib for patients with epithelial ovarian cancer and patients with breast cancer. Analyses included all patients who received at least one dose of the study drugs. The trial is active, but closed to enrolment; follow-up for patients who completed treatment is ongoing. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01623349.
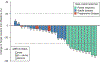
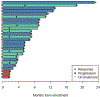
Findings: Between Oct 3, 2014, and Dec 21, 2016, we enrolled 34 patients (28 in the dose-escalation cohort and six in the dose-expansion cohort); two in the dose-escalation cohort were ineligible at the day of scheduled study initiation. Maximum tolerated dose and recommended phase 2 dose were identified as alpelisib 200 mg once a day plus olaparib 200 mg twice a day (dose level 3). Considering all dose levels, the most common treatment-related grade 3-4 adverse events were hyperglycaemia (five [16%] of 32 patients), nausea (three [9%]), and increased alanine aminotransferase concentrations (three [9%]). No treatment-related deaths occurred. Dose-limiting toxic effects included hyperglycaemia and fever with decreased neutrophil count. Of the 28 patients with epithelial ovarian cancer, ten (36%) achieved a partial response and 14 (50%) had stable disease according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors 1.1.
Interpretation: Combining alpelisib and olaparib is feasible with no unexpected toxic effects. The observed activity provides preliminary clinical evidence of synergism between olaparib and alpelisib, particularly in epithelial ovarian cancer, and warrants further investigation.
Funding: Ovarian Cancer Dream Team (Stand Up To Cancer, Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance, National Ovarian Cancer Coalition), Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Novartis.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Extending the scope of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Apr;20(4):470-472. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30019-1. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30880068 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Adavosertib in Combination with Olaparib in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors: An Open-Label, Dose-Finding, and Dose-Expansion Phase Ib Trial.Target Oncol. 2024 Nov;19(6):879-892. doi: 10.1007/s11523-024-01102-8. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Target Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39487373 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rucaparib versus chemotherapy for treatment of relapsed ovarian cancer with deleterious BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation (ARIEL4): final results of an international, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2025 Feb;26(2):249-264. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(24)00674-0. Lancet Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39914419 Clinical Trial.
-
Taxane monotherapy regimens for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD008766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008766.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866378 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors for the treatment of ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 16;2(2):CD007929. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007929.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35170751 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Analysis of EPIK-O/ENGOT-ov61: Alpelisib Plus Olaparib Versus Chemotherapy in Platinum-Resistant or Platinum-Refractory High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Without BRCA Mutation.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Sep 10;43(26):2908-2917. doi: 10.1200/JCO-25-00225. Epub 2025 Jul 23. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40700681 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Paradigm Shift: A Comprehensive Review of Ovarian Cancer Management in an Era of Advancements.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 3;25(3):1845. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031845. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIK3CA Mutations Drive Therapeutic Resistance in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2022 Mar;6:e2100370. doi: 10.1200/PO.21.00370. JCO Precis Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35357905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An effective AKT inhibitor-PARP inhibitor combination therapy for recurrent ovarian cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022 May;89(5):683-695. doi: 10.1007/s00280-022-04403-9. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35419627 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy as a tool to elicit clinically actionable signalling pathways in cancer.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022 Feb;19(2):114-131. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00579-w. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34819622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase Ib Dose Expansion and Translational Analyses of Olaparib in Combination with Capivasertib in Recurrent Endometrial, Triple-Negative Breast, and Ovarian Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 1;27(23):6354-6365. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1656. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34518313 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Matulonis UA, Penson RT, Domchek SM, Kaufman B, Shapira-Frommer R, Audeh MW, et al. Olaparib monotherapy in patients with advanced relapsed ovarian cancer and a germline BRCA1/2 mutation: a multistudy analysis of response rates and safety. Ann Oncol. 2016. June;27(6):1013–9. - PubMed
-
- Mirza MR, Monk BJ, Herrstedt J, Oza AM, Mahner S, Redondo A, et al. Niraparib Maintenance Therapy in Platinum-Sensitive, Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016. December 01;375(22):2154–64. - PubMed
-
- Swisher EM, Lin KK, Oza AM, Scott CL, Giordano H, Sun J, et al. Rucaparib in relapsed, platinum-sensitive high-grade ovarian carcinoma (ARIEL2 Part 1): an international, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016. January;18(1):75–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

