Bilateral Internal Carotid and Left Vertebral Artery Dissection after Blunt Trauma: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 30880295
- PMCID: PMC6465530
- DOI: 10.2176/nmc.cr.2018-0239
Bilateral Internal Carotid and Left Vertebral Artery Dissection after Blunt Trauma: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
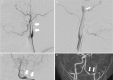
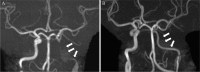
Multi-vessel cervical arterial injury after blunt trauma is rare, and its pathophysiology is unclear. Although blunt cerebrovascular injury is a common cause of cerebral ischemia, its management is still controversial. We describe a 23-year-old man in previously good health who developed three-vessel cervical arterial dissections due to blunt trauma. He was admitted to our emergency and critical care center after a motor vehicle crash. Computed tomography showed a thin, acute subdural hematoma in the right hemisphere and fractures of the odontoid process (Anderson type III), pelvis, and extremities. He was treated conservatively, and about 1 month later, he developed bleariness. Computed tomography angiography showed bilateral internal carotid and left vertebral artery dissection. Aspirin therapy was started immediately, and then clopidogrel was added to the regimen. Two weeks later, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) showed improved blood flow of the vessels. Only aspirin therapy was continued. About 3 months after discharge, MRA demonstrated further improvement of the blood flow of both internal carotid arteries, but the dissection flap on the right side remained. Therefore, we extended the duration of antiplatelet therapy. On the basis of our experience with this case, we think that antithrombotic therapy is crucial for the management of multi-vessel cervical arterial injury, and agents should be used properly according to the injury grade and phase; however, further study is needed to confirm this recommendation.
Keywords: CT angiography; antithrombotic therapy; blunt cerebrovascular injury; dual antiplatelet therapy; motor vehicle crash.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of Cervical Vertebral and Carotid Artery Dissection During Blunt Trauma: Experience From a Level 1 Trauma Center.World Neurosurg. 2020 May;137:e315-e320. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.01.191. Epub 2020 Feb 3. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32028007
-
Bilateral internal carotid and vertebral artery dissection after a horse-riding injury.J Vasc Surg. 2010 Oct;52(4):1052-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.05.065. J Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20888534
-
Asymptomatic carotid artery dissection caused by blunt trauma.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2008 Jan;48(1):22-5. doi: 10.2176/nmc.48.22. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2008. PMID: 18219188
-
Carotid and vertebral arterial dissections in the emergency department.Emerg Med Pract. 2012 Apr;14(4):1-23; quiz 23-4. Emerg Med Pract. 2012. PMID: 22567808 Review.
-
Postpartum internal carotid and vertebral arterial dissections.Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Apr;123(4):848-56. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000189. Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24785614 Review.
Cited by
-
Endovascular treatment of blunt injury of the extracranial internal carotid artery: the prospect and dilemma.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(4):944-952. doi: 10.7150/ijms.50275. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33456352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traumatic Internal Carotid Artery Injuries: Do We Need a Screening Strategy? Literature Review, Case Report, and Forensic Evaluation.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022 Aug 3;20(9):1752-1773. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210712125929. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34254918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequential Bilateral Vertebral Artery Dissections with Prompt Resolution of Initial Insult.Case Rep Neurol. 2020 Jun 11;12(2):189-198. doi: 10.1159/000506766. eCollection 2020 May-Aug. Case Rep Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32647525 Free PMC article.
-
A typically progressive dissection of the internal carotid artery with recurrent hiccups: A case report with continuous 2-year data recording.Ibrain. 2022 Nov 9;9(1):124-129. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12074. eCollection 2023 Spring. Ibrain. 2022. PMID: 37786522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eastman AL, Chason DP, Perez CL, McAnulty AL, Minei JP: Computed tomographic angiography for the diagnosis of blunt cervical vascular injury: is it ready for primetime? J Trauma 60: 925–929, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Goodwin RB, Beery PR, Dorbish RJ, et al. : Computed tomographic angiography versus conventional angiography for the diagnosis of blunt cerebrovascular injury in trauma patients. J Trauma 67: 1046–1050, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Cogbill TH, Moore EE, Meissner M, et al. : The spectrum of blunt injury to the carotid artery: a multicenter perspective. J Trauma 37: 473–479, 1994 - PubMed

