Losartan improves erectile function through suppression of corporal apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats with cavernous nerve injury
- PMID: 30880689
- PMCID: PMC6732892
- DOI: 10.4103/aja.aja_8_19
Losartan improves erectile function through suppression of corporal apoptosis and oxidative stress in rats with cavernous nerve injury
Abstract
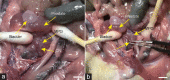
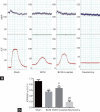
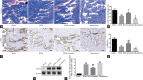
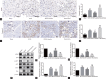
This study aimed to investigate the functional and morphological changes in the corpus cavernosum after cavernous nerve (CN) injury or neurectomy and then reveal whether treatment with the angiotensin II Type 1 receptor antagonist losartan would improve erectile function as well as its potential mechanisms. A total of 48 10-week-old Sprague-Dawley male rats, weighing 300-350 g, were randomly divided into the following four groups (n = 12 per group): sham operation (Sham) group, bilateral cavernous nerve injury (BCNI) group, losartan-treated BCNI (BCNI + Losartan) group, and bilateral cavernous neurectomy (Neurectomy) group. Losartan was administered once daily by oral gavage at a dose of 30 mg kg-1 day-1 for 4 weeks starting on the day of surgery. The BCNI and the Neurectomy groups exhibited decreases in erectile response and increases in apoptosis and oxidative stress, compared with the Sham group. Treatment with losartan could have a modest effect on erectile function and significantly prevent corporal apoptosis and oxidative stress. The phospho-B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)-associated death promoter (p-Bad)/Bad and phospho-the protein kinase B (p-AKT)/AKT ratios were substantially lower, while the Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax)/Bcl-2 ratio, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap-1), transforming growth factor-β 1 (TGF-β 1) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) levels, and caspase-3 activity were higher in the BCNI and Neurectomy groups than in the Sham group. After 4 weeks of daily administration with losartan, these expression levels were remarkably attenuated compared with the BCNI group. Taken together, our results suggested that early administration of losartan after CN injury could slightly improve erectile function and significantly reduce corporal apoptosis and oxidative stress by inhibiting the Akt/Bad/Bax/caspase-3 and Nrf2/Keap-1 pathways.
Keywords: angiotensin II; apoptosis; erectile dysfunction; fibrosis; losartan; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lacosamide alleviates bilateral cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction in the rat model by ameliorating pathological changes in the corpus cavernosum.Int J Impot Res. 2024 May;36(3):283-290. doi: 10.1038/s41443-023-00674-9. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Int J Impot Res. 2024. PMID: 36922697
-
Restoration of erectile function by suppression of corporal apoptosis and oxidative stress with losartan in aged rats with erectile dysfunction.Andrology. 2020 May;8(3):769-779. doi: 10.1111/andr.12757. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Andrology. 2020. PMID: 31968148
-
Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain-derived peptide enhances erectile function by regulating oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells in rats with cavernous nerve injury.Life Sci. 2024 Jul 1;348:122694. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122694. Epub 2024 May 6. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38718855
-
[Exogenous hydrogen sulfide improves erectile dysfunction by inhibiting apoptosis of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells in rats with cavernous nerve injury].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Nov 30;39(11):1329-1336. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.11.10. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31852640 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Administration of H2S improves erectile dysfunction by inhibiting phenotypic modulation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in bilateral cavernous nerve injury rats.Nitric Oxide. 2021 Feb 1;107:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Nitric Oxide. 2021. PMID: 33246103
Cited by
-
Comparison of the therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells on erectile dysfunction in a rat model of bilateral cavernous nerve injury.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 7;10:1019063. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1019063. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36277409 Free PMC article.
-
Buyang Huanwu Decoction Ameliorates Damage of Erectile Tissue and Function Following Bilateral Cavernous Nerve Injury.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Sep;29(9):791-800. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3532-9. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 35679003
-
Lacosamide alleviates bilateral cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction in the rat model by ameliorating pathological changes in the corpus cavernosum.Int J Impot Res. 2024 May;36(3):283-290. doi: 10.1038/s41443-023-00674-9. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Int J Impot Res. 2024. PMID: 36922697
-
Cavernous smooth muscles: innovative potential therapies are promising for an unrevealed clinical diagnosis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2020 Feb;52(2):205-217. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02309-9. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Int Urol Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31617065 Review.
-
Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Mitochondria Transplantation Ameliorated Erectile Dysfunction Induced by Cavernous Nerve Injury.World J Mens Health. 2024 Jan;42(1):188-201. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.220233. Epub 2023 May 23. World J Mens Health. 2024. PMID: 37382278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet. 2013;381:153–65. - PubMed
-
- Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999;84:50–6. - PubMed
-
- Noldus J, Michl U, Graefen M, Haese A, Hammerer P, et al. Patient-reported sexual function after nerve-sparing radical retropubic prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2002;42:118. - PubMed
-
- Burnett AL, Aus G, Canby-Hagino ED, Cookson MS, D’Amico AV, et al. Erectile function outcome reporting after clinically localized prostate cancer treatment. J Urol. 2007;178:597–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

