Optical coherence tomography angiography features in patients with idiopathic full-thickness macular hole, before and after surgical treatment
- PMID: 30880931
- PMCID: PMC6413747
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S189417
Optical coherence tomography angiography features in patients with idiopathic full-thickness macular hole, before and after surgical treatment
Abstract
Purpose: To present optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiography features in patients with idiopathic full-thickness macular hole before and after vitrectomy.
Study design: Prospective case series study.
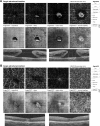
Materials and methods: Patients presenting with an idiopathic full-thickness macular hole (IMH) who underwent posterior vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane peeling and gas tamponade were included in the study. En face OCT and OCT angiography (OCTA) was performed pre- and postoperatively using 3×3 mm scans (Optovue, XR Avanti). Foveal avascular zone (FAZ) area, macular hole size (MHS), central retinal thickness (CRT), macular parafoveal choriocapillary flow area (MCFA), and fovea vessel density (FVDS) were measured and assessed using OCTA. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was examined before and 3 months after surgery.
Results: Twenty-eight eyes of 28 patients were included in the study. The mean age of patient group was 68.28 years. The hole was closed in all eyes after the initial surgery. OCTA showed enlargement of FAZ and increased CRT in foveal area. Mean preoperative FAZ area was 0.39±0.07 mm2. En face images of the middle retina showed a range of preoperative cystic patterns surrounding the hole. BCVA was improved from 0.1±0.11 preoperatively to 0.42±0.17 postoperatively. Mean FAZ area was reduced to 0.24±0.07 mm2 postoperatively with resolution of macular hole and adjacent cystic areas. Mean CRT was reduced from 396±62.6 µm pre-operatively to 272±30.7 µm postoperatively. After vitrectomy, the parafoveal choriocapillary flow area and FVDS of IMH eyes increased compared with the preoperative measurements.
Conclusion: Quantitative evaluation of vascular and morphological changes following IMH surgery using OCTA shows the potential for recovery due to vascular and neuronal plasticity. OCTA showing vascular changes and their quantitative characteristics might be a useful tool for the assessment of macular holes before and after surgical treatment.
Keywords: angio-OCT; central retinal thickness; choriocapillary flow area; foveal avascular zone; foveal vessel density; idopathic full thickness macular hole; imaging; vitrectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
OCT angiography quantifying choriocapillary circulation in idiopathic macular hole before and after surgery.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017 May;255(5):893-902. doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3586-0. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28236003
-
[Relationship between macular hole cavity cross-sectional area and retinal blood flow density and its impact on retinal function in idiopathic macular holes].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Nov 11;59(11):888-898. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112142-20230803-00023. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37936357 Chinese.
-
Changes in the size of the foveal avascular zone after vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane peeling for a macular hole.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017 Nov;61(6):465-471. doi: 10.1007/s10384-017-0529-6. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28785921
-
Microstructural and hemodynamic changes in the fundus after pars plana vitrectomy for different vitreoretinal diseases.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul;262(7):1977-1992. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06303-x. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37982887 Review.
-
Pre- and postoperative OCT features and surgical outcomes of advanced retinitis pigmentosa with macular hole: case series and literature review.BMC Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug 26;24(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03643-y. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39187836 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morphological and Functional Features in Patients with Idiopathic Macular Hole Treatment.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Apr 28;15:4505-4511. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S365886. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35509600 Free PMC article.
-
Morpho-Functional Evaluation of Full-Thickness Macular Holes by the Integration of Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography and Microperimetry.J Clin Med. 2020 Jan 15;9(1):229. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010229. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 31952306 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-regression of idiopathic full-thickness macular holes diameter and anatomical closure rate: Implications to intraoperative technique.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 20;10(17):e36588. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36588. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39263185 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Idiopathic Macular Hole Interventions Using Frequency Domain Optical Coherence Tomography and Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography.Dis Markers. 2022 Aug 13;2022:7749605. doi: 10.1155/2022/7749605. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35996716 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Macular Holes Autologous Retinal Transplant.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 17;12(6):2350. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062350. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36983350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knapp H. Über isolierte zerreissungen der aderhaut in folge von traumen auf dem augapfel. Arch Augenheilkd. 1869;1:6–12.
-
- Collins ET. Unusual changes to the macular region. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK. 1900;20:196–197.
-
- Yaoeda H. Clinical observation on macular hole. Acta Soc Ophthalmol Jpn. 1967;71(9):1723–1736. Japanese. - PubMed
-
- Aaberg TM, Blair CJ, Gass JD. Macular holes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970;69(4):555–562. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

