Management of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current perspectives
- PMID: 30881013
- PMCID: PMC6396653
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S188148
Management of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current perspectives
Abstract
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is a rare disease in Western countries. Nevertheless, its incidence in China, Singapore, and other Eastern countries reaches 20 cases per 100,000 people. Being an extremely chemo- and radiosensitive disease, upfront treatment often consists in the association of intensity-modulated radiation therapy and concurrent cisplatin. Unfortunately, about 20% of the patients suffer from a radioresistant disease which recurs after upfront therapy. For these patients, mainly available therapeutic options consist in systemic therapy, in particular poly-chemotherapy. In those showing a single locoregional recurrence, chemotherapy is not considered to be the preferred approach and other different strategies may be employed. Re-irradiation and surgery are strategies that are always used more often, albeit related to high risk of morbidity. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy, such as heavy ions-based re-irradiations, are experimental but very intriguing options.
Keywords: immunotherapy; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; poly-chemotherapy; radioresistant; re-irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
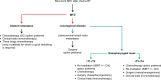
Similar articles
-
Phase I/II trial evaluating concurrent carbon-ion radiotherapy plus chemotherapy for salvage treatment of locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Chin J Cancer. 2016 Dec 22;35(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0164-5. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 28007028 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A triplet chemotherapy regimen of cisplatin, fluorouracil and paclitaxel for locoregionally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma cases contraindicated for re-irradiation/surgery.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;17(12):1585-90. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2016.1204293. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27328125
-
Current Standards for Organ Preservation in Locoregionally Advanced Non-nasopharyngeal Head and Neck Cancer and Evolving Strategies for Favorable-Risk and Platinum-Ineligible Populations.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019 Dec 4;20(12):89. doi: 10.1007/s11864-019-0688-4. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31797157 Review.
-
Radiotherapy-induced anti-tumor immune response and immune-related adverse events in a case of recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing anti-PD-1 immunotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 6;18(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4295-8. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29625593 Free PMC article.
-
Palliative systemic therapy for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma - How far have we achieved?Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017 Jun;114:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.03.030. Epub 2017 Apr 2. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28477740 Review.
Cited by
-
Kinesin superfamily member 15 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 1;27(5):457-470. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2023.27.5.457. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37641808 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cognitive behavioral and psychological intervention on social adaptation, psychological resilience and level of hope in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma in radiotherapy.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jan-Feb;40(1Part-I):95-100. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.1.7421. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38196484 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0028007 Aggravates the Malignancy of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating miR-656-3p/ELF2 Axis.Biochem Genet. 2022 Dec;60(6):2069-2086. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10205-8. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Biochem Genet. 2022. PMID: 35239093
-
Irradiation-induced nasopharyngeal necrosis (INN) in newly diagnosed nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated by intensity-modulated radiation therapy: clinical characteristics and the influence of treatment strategies.Radiat Oncol. 2022 Jan 21;17(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-01980-0. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35062991 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram incorporating neutrophil-to-albumin ratio for predicting overall survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing concurrent chemoradiotherapy.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 3;11(1):e40881. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40881. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39801974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan AT, Teo PM, Johnson PJ. Nasopharyngeal cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2003;114:275–293. - PubMed
-
- Caponigro F, Longo F, Ionna F, Perri F. Treatment approaches to nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a review. Anticancer Drugs. 2010;21(5):471–477. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard P, Lee A, Marguet S, et al. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an update of the MAC-NPC meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(6):645–655. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

