ARQ-197 enhances the antitumor effect of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via decelerating its intracellular clearance
- PMID: 30881018
- PMCID: PMC6396672
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S196713
ARQ-197 enhances the antitumor effect of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via decelerating its intracellular clearance
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the heaviest malignant burdens in China. Molecular targeting agent, sorafenib, is the main therapeutic option for antitumor therapy of advanced HCC, but it is currently too expensive for the public and its therapeutic effect does not satisfy initial expectation. Therefore, it is important to develop more effective molecular targeted therapeutic strategies for advanced HCC.
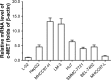
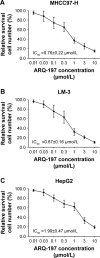
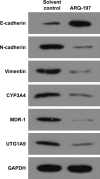
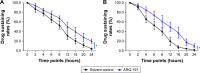
Materials and methods: The antitumor effects of sorafenib or ARQ-197, an antagonist of c-MET (tyrosine-protein kinase Met or hepatocyte growth factor receptor), were examined by MTT or in murine tumor model. The effect of ARQ-197 on epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) or multidrug resistance (MDR) was examined by quantitative real-time PCR for the expression of related genes. The clearance of sorafenib in HCC cells was detected by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry.
Results: ARQ-197 treatment enhanced the sensitivity of HCC cells to sorafenib. Mechanistic studies indicated that ARQ-197 inhibited the expression of EMT- and MDR-related genes. Moreover, ARQ-197 treatment decelerated the clearance of sorafenib in cultured HCC cells and subcutaneous HCC tumors in nude mice.
Conclusion: In the present work, our data suggested that ARQ-197 decelerated the clearance of sorafenib in HCC cells and enhanced the antitumor effect of sorafenib.
Keywords: ARQ-197 and sorafenib; advanced hepatocellular carcinoma; drug clearance; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; molecular targeted agents; multidrug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/snail signaling pathway contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition-induced multi-drug resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 21;12(9):e0185088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185088. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28934275 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-140-3p enhances the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib by targeting pregnenolone X receptor.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Sep 17;11:5885-5894. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S179509. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30271172 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of AKT Inhibitor ARQ 092 Compared with Sorafenib in a Cirrhotic Rat Model with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Oct;16(10):2157-2165. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0602-T. Epub 2017 May 31. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28566435
-
Tivantinib: critical review with a focus on hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014 Nov;23(11):1563-74. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2014.949339. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25307444 Review.
-
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: A Mediator of Sorafenib Resistance in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017;17(8):698-706. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666170427104356. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 28460616 Review.
Cited by
-
Foretinib Inhibits Cancer Stemness and Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation by Decreasing CD44 and c-MET Signaling.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Feb 3;13:1027-1035. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S226951. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32099405 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in elucidating the mechanisms of Sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Surg. 2025 Apr 1;111(4):2990-3005. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002294. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39992113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypermethylation of the Promoter Region of miR-23 Enhances the Metastasis and Proliferation of Multiple Myeloma Cells via the Aberrant Expression of uPA.Front Oncol. 2022 May 30;12:835299. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.835299. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35707350 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation integratedly modulates the expression of Pit-Oct-Unt transcription factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 15;12(6):1634-1643. doi: 10.7150/jca.49231. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33613750 Free PMC article.
-
Tivantinib, A c-Met Inhibitor in Clinical Trials, Is Susceptible to ABCG2-Mediated Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 12;12(1):186. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010186. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31940916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Razavi-Shearer D, Gamkrelidze I, Nguyen MH, Polaris Observatory Collaborators Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(6):383–403. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Wang F, Zhang Z. Current advances in the elimination of hepatitis B in China by 2030. Front Med. 2017;11(4):490–501. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

