Ultrasound-guided serratus anterior plane block for analgesia after thoracic surgery
- PMID: 30881105
- PMCID: PMC6417847
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S191263
Ultrasound-guided serratus anterior plane block for analgesia after thoracic surgery
Abstract
Background: Patients who undergo surgical procedures that impair the integrity of the chest wall frequently experience extremely severe postoperative pain. Opiates and weaker analgesics, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are not sufficiently effective in achieving control of severe pain and might cause respiratory and gastrointestinal complications. In the past decade, there has been an increased interest in the use of regional nerve blocks for post-thoracoscopy and post-thoracotomy analgesia.
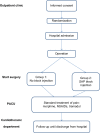
Methods: This is a prospective, randomized, double-blind and single-center study. We recruited 104 patients who underwent elective thoracoscopy. Prior to surgery, the participating patients were randomized into one of two study groups: Group 1- the "standard control group" that received standard postoperative pain control with intravenous opioids, NSAIDs and acetaminophen (paracetamol) and Group 2- the "block group" that was treated by ultrasound-guided serratus anterior plane (SAP) block (a single injection of 0.25% bupivacaine hydrochloride 2 mg/kg plus dexamethasone 8 mg) with standard postoperative pain control regimen. We compared the clinical, laboratory, and postoperative pain assessment data of both groups.
Results: Patients in the SAP block Group 2 reported significantly lower levels of pain after thoracic surgery as assessed by their visual analog scale scores, as compared to the patients in the standard pain control Group 1 (P<0.001). The total dosage of morphine and tramadol required for pain relief during the first hours after surgery was significantly lower in the patients who received SAP block. Also, the incidence of vomiting after surgery was significantly lower among the patients who received SAP block than among the patients who received standard pain control.
Conclusion: The results of the present study suggest that SAP block is an effective adjuvant treatment option for post-thoracic surgery analgesia. Compared to the current methods used for post-thoracic surgery pain relief, SAP block has some significant merits, particularly its ease of use and its low potential for side effects.
Keywords: post-thoracic surgery pain relief; post-thoracotomy analgesia; serratus anterior plane block; thoracic surgery; thoracoscopy; ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of Ultrasound-Guided Interfascial Plane Blocks in Anterior and Lateral Thoracic Wall Region as Safe Method for Patient Anesthesia and Analgesia: Review of Techniques and Approaches during COVID-19 Pandemic.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 17;19(14):8696. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148696. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35886547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of ultrasound-guided second serratus anterior plane block on postoperative quality of recovery and analgesia after video-assisted thoracic surgery: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled study.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Jul 30;16(7):4195-4207. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-982. Epub 2024 Jul 18. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 39144345 Free PMC article.
-
Serratus Anterior Plane (SAP) Block Used for Thoracotomy Analgesia: A Case Report.Korean J Pain. 2016 Jul;29(3):189-92. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.3.189. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Korean J Pain. 2016. PMID: 27413485 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of analgesic efficacy of ultrasound-guided thoracic paravertebral block versus surgeon-guided serratus anterior plane block for acute postoperative pain in patients undergoing thoracotomy for lung surgery-A prospective randomized study.Saudi J Anaesth. 2020 Oct-Dec;14(4):423-430. doi: 10.4103/sja.SJA_143_20. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Saudi J Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 33447181 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic Effectiveness of Perioperative Ultrasound-Guided Serratus Anterior Plane Block Combined with General Anesthesia in Patients Undergoing Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Pain Med. 2020 Oct 1;21(10):2412-2422. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnaa125. Pain Med. 2020. PMID: 32488265
Cited by
-
PROSPECT guidelines for video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: a systematic review and procedure-specific postoperative pain management recommendations.Anaesthesia. 2022 Mar;77(3):311-325. doi: 10.1111/anae.15609. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Anaesthesia. 2022. PMID: 34739134 Free PMC article.
-
Erector Spinae Plane Block Combined with Serratus Anterior Plane Block Versus Thoracic Paravertebral Block for Postoperative Analgesia and Recovery After Thoracoscopic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Non-inferiority Clinical Trial.Curr Med Sci. 2023 Jun;43(3):615-622. doi: 10.1007/s11596-023-2745-2. Epub 2023 May 26. Curr Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37233969 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of Ultrasound-Guided Interfascial Plane Blocks in Anterior and Lateral Thoracic Wall Region as Safe Method for Patient Anesthesia and Analgesia: Review of Techniques and Approaches during COVID-19 Pandemic.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 17;19(14):8696. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148696. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35886547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Ropivacaine Concentration on Analgesia After Ultrasound-Guided Serratus Anterior Plane Block: A Randomized Double-Blind Trial.J Pain Res. 2020 Jan 10;13:57-64. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S229523. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 32021395 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Serratus Anterior Plane Block After Video-Assisted Lung Wedge Resection: A Single-Center, Prospective, and Randomized Controlled Trial.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 26;61(1):11. doi: 10.3390/medicina61010011. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39858993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous