Spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension is caused by a decrease in stroke volume in elderly patients
- PMID: 30881108
- PMCID: PMC6404676
- DOI: 10.2147/LRA.S193925
Spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension is caused by a decrease in stroke volume in elderly patients
Abstract
Background: Hypotension is common during spinal anesthesia (SA) and is caused by a decrease in systemic vascular resistance (SVR) and/or cardiac output (CO). The effect of the dose of bupivacaine administered intrathecally on the changes in CO in elderly patients is largely unknown. This study investigated the hemodynamic effect of SA in elderly patients by studying the effect of two different dosages of intrathecal bupivacaine.
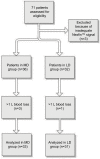
Methods: This prospective cohort study included 64 patients aged >65 years scheduled for procedures under SA; the patients received either 15 mg bupivacaine (the medium dose [MD] group) or 10 mg bupivacaine and 5 μg sufentanil (the low dose [LD] group). Blood pressure and CO were monitored throughout the procedure using Nexfin™, a noninvasive continuous monitoring device using a finger cuff.
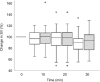
Results: Thirty-three patients received MD and 31 received LD and there was no mean difference in baseline hemodynamics between the groups. On an average, the CO decreased 11.6% in the MD group and 10.0 % in the LD group. There was no significant change in SVR. Incidence of a clinically relevant decrease in stroke volume (SV) (>15% from baseline) was 67% in the MD and 45% in the LD groups (P<0.05).
Conclusion: CO and blood pressure decreased significantly after the onset of SA in elderly patients. This is mainly caused by a decrease in SV and not by a decrease in SVR. There was no difference in CO and blood pressure change between dosages of 10 or 15 mg bupivacaine.
Keywords: cardiac output; dose; finger blood pressure measurement; intrathecal anesthesia; local anesthetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemodynamic effects of intrathecal sufentanil compared with epidural bupivacaine in laboring parturients.J Clin Anesth. 1996 Sep;8(6):497-501; discussion 502-3. doi: 10.1016/0952-8180(96)00106-7. J Clin Anesth. 1996. PMID: 8872691 Clinical Trial.
-
Small-dose bupivacaine-sufentanil prevents cardiac output modifications after spinal anesthesia.Anesth Analg. 2005 Nov;101(5):1512-1515. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000180996.91358.CC. Anesth Analg. 2005. PMID: 16244022 Clinical Trial.
-
Relationship between changes in regional cerebral blood volume and oxygenation and changes in cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance during spinal anesthesia in women undergoing cesarean section.J Anesth. 2019 Oct;33(5):579-586. doi: 10.1007/s00540-019-02670-0. Epub 2019 Aug 7. J Anesth. 2019. PMID: 31392418
-
Spinal anesthesia using single injection small-dose bupivacaine versus continuous catheter injection techniques for surgical repair of hip fracture in elderly patients.Anesth Analg. 2006 May;102(5):1559-63. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000218421.18723.cf. Anesth Analg. 2006. PMID: 16632842 Clinical Trial.
-
Hypotension from spinal anesthesia in patients aged greater than 80 years is due to a decrease in systemic vascular resistance.J Clin Anesth. 2012 May;24(3):201-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2011.07.014. J Clin Anesth. 2012. PMID: 22537572
Cited by
-
Preoperative echocardiography as a predictor of spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension in older patients with mild left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: a retrospective observational study.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2024 Apr;19(2):134-143. doi: 10.17085/apm.23161. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 38725168 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation Effect of Aspiration of 0.2 ml of Cerebrospinal Fluid After Completion of Injection 0.5% Bupivacaine and Reinjection Into Subarachnoid Space on Sensory and Motor Block in Cesarean Section: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 25;9:816974. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.816974. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35402445 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation, combined spinal-epidural anesthesia, and general anesthesia with laryngeal mask airway and nerve block for intertrochanteric fracture surgeries in elderly patients: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Dec 17;19(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0908-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 31847846 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal Injection of Hyperbaric Bupivacaine Versus a Mixture of Hyperbaric and Isobaric Bupivacaine in Lower Abdominal Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Anesth Pain Med. 2024 Jan 3;13(6):e142719. doi: 10.5812/aapm-142719. eCollection 2023 Dec. Anesth Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 38721440 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utility of ultrasonography, pulse oximetry and arterial line derived hemodynamic parameters for predicting post-induction hypotension in patients undergoing elective craniotomy for excision of brain tumors - A prospective observational study.Heliyon. 2022 Oct 22;8(11):e11208. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11208. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36339752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpenter RL, Caplan RA, Brown DL, Stephenson C, Wu R. Incidence and risk factors for side effects of spinal anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1992;76(6):906–916. - PubMed
-
- Hartmann B, Junger A, Klasen J, et al. The incidence and risk factors for hypotension after spinal anesthesia induction: an analysis with automated data collection. Anesth Analg. 2002;94(6):1521–1529. table of contents. - PubMed
-
- Salinas FV, Sueda LA, Liu SS. Physiology of spinal anaesthesia and practical suggestions for successful spinal anaesthesia. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2003;17(3):289–303. - PubMed
-
- Langesaeter E, Rosseland LA, Stubhaug A. Continuous invasive blood pressure and cardiac output monitoring during cesarean delivery: a randomized, double-blind comparison of low-dose versus high-dose spinal anesthesia with intravenous phenylephrine or placebo infusion. Anesthesiology. 2008;109(5):856–863. - PubMed
-
- Asehnoune K, Larousse E, Tadié JM, Minville V, Droupy S, Benhamou D. Small-dose bupivacaine-sufentanil prevents cardiac output modifications after spinal anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2005;101(5):1512–1515. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

