Perampanel Affects Up-Stream Regulatory Signaling Pathways of GluA1 Phosphorylation in Normal and Epileptic Rats
- PMID: 30881292
- PMCID: PMC6405474
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00080
Perampanel Affects Up-Stream Regulatory Signaling Pathways of GluA1 Phosphorylation in Normal and Epileptic Rats
Abstract
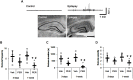
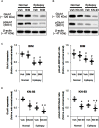
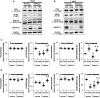
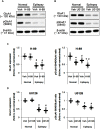
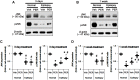
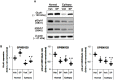
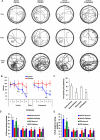
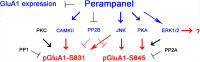
To elucidate the pharmacological properties of perampanel [2-(2-oxo-1-phenyl-5-pyridin-2-yl-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)benzonitrile, a novel non-competitive antagonist of AMPA receptor], we investigated its effects on the up-stream regulatory pathways of GluA1 phosphorylation including protein kinase C (PKC), Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII), protein kinase A (PKA), extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), protein phosphatase (PP) 1, PP2A, and PP2B in normal and pilocarpine-induced epileptic rat model using Western blot analysis. In normal animals, perampanel affected GluA1 expression/phosphorylation, PKC, CAMKII, PKA, ERK1/2, JNK, and PPs activities. In epileptic rats, perampanel effectively inhibited spontaneous seizure activities. Perampanel enhanced phospho (p)-GluA1-S831 and -S845 ratios (phosphoprotein/total protein), while it reduced GluA1 expression. Perampanel also increased pCAMKII and pPKA ratios, which phosphorylate GluA1-S831 and -S845 site, respectively. Perampanel elevated pJNK and pPP2B ratios, which phosphorylates and dephosphorylates both GluA1-S831 and -S845 sits. Perampanel also increased pERK1/2 ratio in epileptic animals, while U0126 (an ERK1/2 inhibitor) did not affect pGluA1 ratios. Perampanel did not influence PKC, PP1, and PP2A expression levels and their phosphorylation ratios. In addition, perampanel did not have a detrimental impact on cognitive abilities of epileptic and normal rats in Morris water maze test. These findings suggest that perampanel may regulate AMPA receptor functionality via not only blockade of AMPA receptor but also the regulations of multiple molecules (CAMKII, PKA, JNK, and pPP2B)-mediated GluA1 phosphorylations without negative effects on cognition, although the effects of perampanel on PKC, PP1, and PP2A activities were different between normal and epileptic rats.
Keywords: BIM; CAMKII; ERK1/2; H-89; JNK; KN-93; cyclosporin A; okadaic acid.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Blockade of AMPA Receptor Regulates Mitochondrial Dynamics by Modulating ERK1/2 and PP1/PP2A-Mediated DRP1-S616 Phosphorylations in the Normal Rat Hippocampus.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 May 1;13:179. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00179. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31118889 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitors disrupt AKAP79-dependent PKC signaling to GluA1 AMPA receptors.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):6697-706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.183558. Epub 2010 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21156788 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic increases in AMPA receptor phosphorylation in the rat hippocampus in response to amphetamine.J Neurochem. 2015 Jun;133(6):795-805. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13067. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25689263 Free PMC article.
-
Perampanel, a novel, non-competitive, selective AMPA receptor antagonist as adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant partial-onset seizures.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013 Feb;14(2):225-35. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2013.754883. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23259931 Review.
-
Perampanel.2023 Dec 15. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006–. 2023 Dec 15. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; 2006–. PMID: 29999805 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) 1 succinylation modulates epileptic seizures and the blood-brain barrier.Exp Anim. 2023 Nov 9;72(4):475-489. doi: 10.1538/expanim.23-0019. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Exp Anim. 2023. PMID: 37258131 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Aging, Circular RNAs, and RNA Editing in the Pathogenesis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Cells. 2023 May 22;12(10):1443. doi: 10.3390/cells12101443. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF/Cyclin D1 Signaling System and Cognitive Performance After Perampanel and Lacosamide Treatment Singly or in Combination in an Experimental Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 11;46(12):14010-14032. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120838. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727966 Free PMC article.
-
CDDO-Me Attenuates Astroglial Autophagy via Nrf2-, ERK1/2-SP1- and Src-CK2-PTEN-PI3K/AKT-Mediated Signaling Pathways in the Hippocampus of Chronic Epilepsy Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;10(5):655. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050655. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922531 Free PMC article.
-
The role of peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 in neuronal signaling in epilepsy.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 11;15:1006419. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1006419. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36304997 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn S. M., Choe E. S. (2009). Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors increases serine phosphorylation of GluR1 alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors in the rat dorsal striatum. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 329 1117–1126. 10.1124/jpet.108.149542 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

