Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid-Based Therapy Attenuates the Progression of Postischemic Heart Failure in Normotensive Sprague-Dawley but Not in Hypertensive Ren-2 Transgenic Rats
- PMID: 30881303
- PMCID: PMC6406051
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00159
Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid-Based Therapy Attenuates the Progression of Postischemic Heart Failure in Normotensive Sprague-Dawley but Not in Hypertensive Ren-2 Transgenic Rats
Abstract
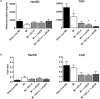
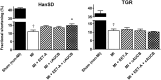
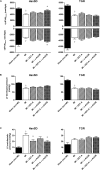
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and their analogs have been identified as potent antihypertensive compounds with cardio- and renoprotective actions. Here, we examined the effect of EET-A, an orally active EET analog, and c-AUCB, an inhibitor of the EETs degrading enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase, on the progression of post-myocardial infarction (MI) heart failure (HF) in normotensive Hannover Sprague-Dawley (HanSD) and in heterozygous Ren-2 transgenic rats (TGR) with angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Adult male rats (12 weeks old) were subjected to 60-min left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery occlusion or sham (non-MI) operation. Animals were treated with EET-A and c-AUCB (10 and 1 mg/kg/day, respectively) in drinking water, given alone or combined for 5 weeks starting 24 h after MI induction. Left ventricle (LV) function and geometry were assessed by echocardiography before MI and during the progression of HF. At the end of the study, LV function was determined by catheterization and tissue samples were collected. Ischemic mortality due to the incidence of sustained ventricular fibrillation was significantly higher in TGR than in HanSD rats (35.4 and 17.7%, respectively). MI-induced HF markedly increased LV end-diastolic pressure (Ped) and reduced fractional shortening (FS) and the peak rate of pressure development [+(dP/dt)max] in untreated HanSD compared to sham (non-MI) group [Ped: 30.5 ± 3.3 vs. 9.7 ± 1.3 mmHg; FS: 11.1 ± 1.0 vs. 40.8 ± 0.5%; +(dP/dt)max: 3890 ± 291 vs. 5947 ± 309 mmHg/s]. EET-A and c-AUCB, given alone, tended to improve LV function parameters in HanSD rats. Their combination amplified the cardioprotective effect of single therapy and reached significant differences compared to untreated HanSD controls [Ped: 19.4 ± 2.2 mmHg; FS: 14.9 ± 1.0%; +(dP/dt)max: 5278 ± 255 mmHg/s]. In TGR, MI resulted in the impairment of LV function like HanSD rats. All treatments reduced the increased level of albuminuria in TGR compared to untreated MI group, but neither single nor combined EET-based therapy improved LV function. Our results indicate that EET-based therapy attenuates the progression of post-MI HF in HanSD, but not in TGR, even though they exhibited renoprotective action in TGR hypertensive rats.
Keywords: chronic heart failure; echocardiography; epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; hypertension; myocardial infarction; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid analog EET-B attenuates post-myocardial infarction remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 Apr 29;133(8):939-951. doi: 10.1042/CS20180728. Print 2019 Apr 30. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30979784 Free PMC article.
-
Vasodilatory responses of renal interlobular arteries to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids analog are not enhanced in Ren-2 transgenic hypertensive rats: evidence against a role of direct vascular effects of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in progression of experimental heart failure.Physiol Res. 2017 Mar 31;66(1):29-39. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.933350. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Physiol Res. 2017. PMID: 27782740
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase by cis-4-[4-(3-adamantan-1-ylureido)cyclohexyl-oxy]benzoic acid exhibits antihypertensive and cardioprotective actions in transgenic rats with angiotensin II-dependent hypertension.Clin Sci (Lond). 2012 Jun;122(11):513-25. doi: 10.1042/CS20110622. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22324471 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase is renoprotective in 5/6 nephrectomized Ren-2 transgenic hypertensive rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014 Mar;41(3):227-37. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12204. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24471737 Free PMC article.
-
Two pharmacological epoxyeicosatrienoic acid-enhancing therapies are effectively antihypertensive and reduce the severity of ischemic arrhythmias in rats with angiotensin II-dependent hypertension.J Hypertens. 2018 Jun;36(6):1326-1341. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001708. J Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 29570510 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of Epoxide Hydrolase 2 Gene Arg287Gln with the Risk for Primary Hypertension in Chinese.Int J Hypertens. 2020 Feb 28;2020:2351547. doi: 10.1155/2020/2351547. eCollection 2020. Int J Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32181010 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CYP-sEH derived lipid mediators in regulating mitochondrial biology and cellular senescence: implications for the aging heart.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;15:1486717. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1486717. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39703395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Endogenous Activity of the Renin-Angiotensin System Reduces Infarct Size in the Rats with Early Angiotensin II-dependent Hypertension which Survive the Acute Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 28;12:679060. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.679060. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34122103 Free PMC article.
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid analog EET-B attenuates post-myocardial infarction remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 Apr 29;133(8):939-951. doi: 10.1042/CS20180728. Print 2019 Apr 30. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30979784 Free PMC article.
-
Epoxylipids and soluble epoxide hydrolase in heart diseases.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Jan;195:114866. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114866. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34863976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alánová P., Husková Z., Kopkan L., Sporková A., Jíchová Š, Neckář J., et al. (2015). Orally active epoxyeicosatrienoic acid analog does not exhibit antihypertensive and reno- or cardioprotective actions in two-kidney, one-clip Goldblatt hypertensive rats. Vascul. Pharmacol. 73 45–56. 10.1016/j.vph.2015.08.013 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

