Vitamin D Insufficiency in Overweight and Obese Children and Adolescents
- PMID: 30881343
- PMCID: PMC6406072
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00103
Vitamin D Insufficiency in Overweight and Obese Children and Adolescents
Abstract
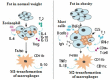
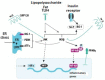
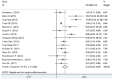
Excessive body weight and obesity in childhood and adolescence are becoming more and more important unfavorable factors that entail extremely adverse consequences and require close attention of physicians of any specialty. Along with the high prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome in pediatric patients, children and adolescents in the majority of countries are diagnosed with vitamin D deficiency. Among the non-calcaemic effects of vitamin D, a significant role is played by its impact on the hormonal regulation of glucose metabolism and the synthesis of adipokines by fat tissue. The review presents literature data indicative of a close pathogenic relationship between vitamin D insufficiency and impaired tissue insulin sensitivity. It demonstrates the role of vitamin D insufficiency in immune reactions resulting in development of subclinical inflammation in fat tissue infiltrated with macrophages and lymphocytes. It also shows the role of adipokines, immune system cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines produced by them in the pathogenesis of obesity, as well as the function of vitamin D as an endocrine and paracrine regulator of the process of inflammation in adipose tissue. The relationships between the principal adipokines (leptin, adiponectin, resistin) are revealed in the presence of normal vitamin D content and in vitamin D deficiency. The carbohydrate and lipid metabolism parameters in overweight children and adolescents with vitamin D insufficiency are analyzed. A high prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in overweight and obese children and adolescents (increasing along with the severity of obesity) is demonstrated. The review also presents the current recommendations for the correction of vitamin D insufficiency and underlines the need for higher cholecalciferol doses to achieve serum calcifediol targets in overweight and obese children and adolescents.
Keywords: adipose tissue and autoimmune inflammation; child obesity; vitamin D; vitamin D and obesity; vitamin D and obesity in children.
Figures


References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, et al. . National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9·1 million participants. Lancet (2011) 377:557–67. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, Danaei G, Shibuya K, Adair-Rohani H, et al. . A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (2012) 380:2224–60. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

