The Tissue Distribution of Four Major Coumarins after Oral Administration of Angelicae Pubescentis Radix Extract to Rats Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
- PMID: 30881472
- PMCID: PMC6383424
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2365697
The Tissue Distribution of Four Major Coumarins after Oral Administration of Angelicae Pubescentis Radix Extract to Rats Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
Angelicae pubescentis radix (APR) is widely applied in treating rheumatoid arthritis in China. Coumarins are the major active compounds of APR extract including columbianetin, columbianetin acetate, osthole, and columbianadin. The in vivo behavior of the four major coumarins of APR has not been systematically reported. A feasible and reliable ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) method was established and validated for the quantification of the above four coumarins in rat various tissues (including heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, uterus, ovary, and muscle) after oral administration of APR extract. The separation was implemented on a Waters ACQUITY BEH C18 column (4.6 mm × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) with gradient mobile phase comprising acetonitrile-water (with 1mM formic acid) at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. The tissue homogenate samples were prepared by liquid-liquid extraction with ethyl acetate. The calibration curves were linear in the range of 1.6-20000 ng/mL for four coumarins with the lower limit of quantitation of 1.6 ng/mL in rat tissues. The intraday and interday precisions and recoveries were all within 80-100% with the relative standard deviations (RSDs) which were all less than 10.9%. The method was successfully applied to the tissue distribution research after oral administration of 6.0 g/kg APR extract to rat. The results revealed that the tissues distributions of four coumarins were in the liver, followed by the ovary, uterus, kidney, lung, heart, spleen, and muscle.
Figures
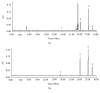
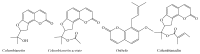
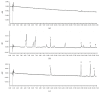
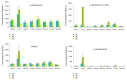
Similar articles
-
Distribution Assessments of Coumarins from Angelicae Pubescentis Radix in Rat Cerebrospinal Fluid and Brain by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis.Molecules. 2018 Jan 20;23(1):225. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010225. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29361720 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous assessment of absorption characteristics of coumarins from Angelicae Pubescentis Radix: In vitro transport across Caco-2 cell and in vivo pharmacokinetics in rats after oral administration.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017 Aug 15;1060:308-315. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.06.020. Epub 2017 Jun 13. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28654868
-
Simultaneous determination of scopoletin, psoralen, bergapten, xanthotoxin, columbianetin acetate, imperatorin, osthole and isoimperatorin in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS for pharmacokinetic studies following oral administration of Radix Angelicae Pubescentis extract.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Apr 15;77:71-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2012.12.031. Epub 2013 Jan 5. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23384552
-
Simultaneous Determination of Columbianadin and Its Metabolite Columbianetin in Rat Plasma by LC-MS/MS: Application to Pharmacokinetics of Columbianadin after Oral Administration.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Sep 19;2018:8568303. doi: 10.1155/2018/8568303. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30327682 Free PMC article.
-
Separation and Enrichment of Three Coumarins from Angelicae Pubescentis Radix by Macroporous Resin with Preparative HPLC and Evaluation of Their Anti-Inflammatory Activity.Molecules. 2019 Jul 23;24(14):2664. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142664. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31340484 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Columbianetin alleviates lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced inflammation and apoptosis in chondrocyte through activation of autophagy by inhibiting serum and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 1 (SGK1) expression.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):4051-4062. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2032970. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35129051 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine of Angelicae Pubescentis Radix: A Review of Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 18;11:335. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00335. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32256373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer potential of osthole: targeting gynecological tumors and breast cancer.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Feb;77(1):87-102. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00685-3. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39617816 Review.
-
Study on Absorption, Distribution and Excretion of a New Candidate Compound XYY-CP1106 against Alzheimer's Disease in Rats by LC-MS/MS.Molecules. 2023 Mar 4;28(5):2377. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052377. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903623 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Columbianadin, a Bioactive Coumarin Derivative, in Perturbing Transient and Persistent INa.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 9;22(2):621. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020621. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He T. T., Zhou W., Ren J. Scientific research on traditional Chinese medicine from the perspective of viscera-state theory. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine & Pharmacy. 2017;32(2):420–423.
-
- Gu G. G. Divine Farmer’s Classic of Material Medica. Beijing, China: People's Medical Publishing House; 1955.
-
- Yang X. Extraction and content determination studies on the basis of Radix Angelicae Pubescentis. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal. 2013;25(6):13–16.
-
- Pan J. X., Lam Y. K., Arison B., Smith J., Han G. Q. Isolation and identification of isoangelol, anpubesol and other coumarins from Angelica pubescens Maxim. Acta Pharmaceutica Sciencia. 1987;22(5):380–384. - PubMed
-
- Li Y. L., Gao M. H. Determination of Osthole and Columbianctim in AngeHca Pubescens Maxim. F. biserrata Shan et Yuan by RP—HPLC. Guide of China Medicine. 2010;8(19):59–60.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

