Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction: A Technical Algorithm
- PMID: 30881836
- PMCID: PMC6416134
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002107
Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction: A Technical Algorithm
Abstract
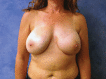
Despite falling out of favor in the 1970s, prepectoral breast reconstruction has resurfaced in the recent years as a safe and effective alternative to subpectoral/partial subpectoral breast reconstruction in carefully selected patients. This article outlines an algorithmic technical approach to prepectoral breast reconstruction for new patients and revision patients.
Figures








References
-
- Nahabedian MY, Glasberg SB, Maxwell GP. Introduction to “prepectoral breast reconstruction.” Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140:4S–5S. - PubMed
-
- Nahabedian MY, Cocilovo C. Two-stage prosthetic breast reconstruction: a comparison between prepectoral and partial subpectoral techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140:22S–30S. - PubMed
-
- Sigalove S. Options in acellular dermal matrix-device assembly. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140:39S–42S. - PubMed
-
- Sigalove S, Maxwell GP, Sigalove NM, et al. Prepectoral implant-based breast reconstruction: rationale, indications, and preliminary results. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Storm-Dickerson T, Sigalove N. Prepectoral breast reconstruction: the breast surgeon’s perspective. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;140:43S–48S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
