Combination of Intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guérin and Chemotherapy vs. Bacille Calmette-Guérin Alone in Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30881921
- PMCID: PMC6405446
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00121
Combination of Intravesical Bacille Calmette-Guérin and Chemotherapy vs. Bacille Calmette-Guérin Alone in Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: About 75% of newly diagnosed bladder cancer cases suffer from non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), which used to recur and progress despite transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT). This meta-analysis was conducted to examine if combined application of intravesical bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) with chemotherapy is associated with better prognosis. Methods: Systematic searches of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) concerning NMIBC were performed in PubMed, EMbase, CENTRAL, CNKI, WanFang, VIP, CBM databases, and some specialized websites. Two researchers independently implemented study selection, quality assessment and data extraction. Hazard ratios (HRs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for treatment effects on recurrence-free survival (RFS), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and disease-specific survival (DSS) were directly extracted, if available, or estimated using relevant data from included studies. Side effects, such as fever, gastrointestinal reaction, cystitis, irritative bladder symptoms and hematuria, were also extracted as outcome measurements, and associated relative risks (RRs) were calculated to assess treatment safety. RevMan 5.3 software was used to perform statistical analyses. Results: Thirteen RCTs containing 1,754 patients with NMIBC were included in this meta-analysis. Compared with BCG alone, the combination therapy significantly improved RFS (HR = 0.53, 95% CI: 0.43-0.66, P < 0.01), OS (HR = 0.66, 95%CI: 0.50-0.86, P = 0.002), and DSS (HR = 0.48, 95%CI: 0.29-0.80, P = 0.005). While PFS showed no obvious difference between combination therapy and BCG alone (HR = 0.65, 95%CI: 0.25-1.68, P = 0.38). The rate of fever (RR = 0.50, 95%CI: 0.27-0.91, P = 0.02), irritative bladder symptoms (RR = 0.69, 95%CI: 0.52-0.90, P = 0.007) and hematuria (RR = 0.50, 95%CI: 0.28-0.89, P = 0.02) were significantly decreased in patients treated with combination therapy compared to those with BCG alone. There were no statistically significant differences between combination therapy and BCG alone in toxicity (RR = 0.69, 95%CI: 0.34-1.40, P = 0.30), gastrointestinal reaction (RR = 2.54, 95%CI: 0.61-10.60, P = 0.20) or cystitis (RR = 0.67, 95%CI: 0.29-1.54, P = 0.34). Conclusions: Combined application of intravesical BCG and chemotherapy appears to be an effective treatment for patients with intermediate- to high-risk NMIBC, but not for those with tumor in situ alone or recurrent bladder cancer.
Keywords: bacille Calmette-Guérin; chemotherapy; meta-analysis; non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; prognosis.
Figures
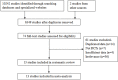
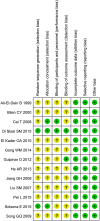





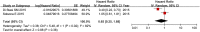

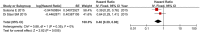




Similar articles
-
Intravesical Therapy for the Treatment of Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Urol. 2017 May;197(5):1189-1199. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2016.12.090. Epub 2016 Dec 24. J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28027868
-
The efficacy and safety of intravesical gemcitabine vs Bacille Calmette-Guérin for adjuvant treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Aug 8;11:4641-4649. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S170477. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30122955 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of intraarterial chemotherapy for non muscle invasive bladder cancer: Promising alternative therapy in high tuberculosis burden countries.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2024 Feb 16;96(1):12154. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2024.12154. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2024. PMID: 38363237
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Hyperthermia Intravesical Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Urol Int. 2024;108(4):322-333. doi: 10.1159/000538373. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Urol Int. 2024. PMID: 38508149
-
Efficacy and toxicity in scheduled intravesical gemcitabine versus Bacille Calmette-Guérin for Ta and T1 bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Jun;10(6):2849-2858. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-291. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116595 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-Muscular Invasive Bladder Cancer: Re-envisioning Therapeutic Journey from Traditional to Regenerative Interventions.Aging Dis. 2021 Jun 1;12(3):868-885. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.1109. eCollection 2021 Jun. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 34094648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Therapy for Bladder Cancer: An Update.Immunotargets Ther. 2020 Feb 13;9:1-11. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S202006. eCollection 2020. Immunotargets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32104666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cuprous oxide nanoparticles trigger reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis through activation of erk-dependent autophagy in bladder cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 May 14;11(5):366. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2554-5. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32409654 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing Treatment: Breakthrough Approaches for BCG-Unresponsive Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 30;16(7):1366. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071366. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvant therapies for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: advances during BCG shortage.World J Urol. 2022 May;40(5):1111-1124. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03908-x. Epub 2022 Jan 27. World J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35083522 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

