MuSK myasthenia gravis monoclonal antibodies: Valency dictates pathogenicity
- PMID: 30882021
- PMCID: PMC6410930
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000547
MuSK myasthenia gravis monoclonal antibodies: Valency dictates pathogenicity
Abstract
Objective: To isolate and characterize muscle-specific kinase (MuSK) monoclonal antibodies from patients with MuSK myasthenia gravis (MG) on a genetic and functional level.
Methods: We generated recombinant MuSK antibodies from patient-derived clonal MuSK-specific B cells and produced monovalent Fab fragments from them. Both the antibodies and Fab fragments were tested for their effects on neural agrin-induced MuSK phosphorylation and acetylcholine receptor (AChR) clustering in myotube cultures.
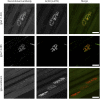
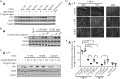
Results: The isolated MuSK monoclonal antibody sequences included IgG1, IgG3, and IgG4 that had undergone high levels of affinity maturation, consistent with antigenic selection. We confirmed their specificity for the MuSK Ig-like 1 domain and binding to neuromuscular junctions. Monovalent MuSK Fab, mimicking functionally monovalent MuSK MG patient Fab-arm exchanged serum IgG4, abolished agrin-induced MuSK phosphorylation and AChR clustering. Surprisingly, bivalent monospecific MuSK antibodies instead activated MuSK phosphorylation and partially induced AChR clustering, independent of agrin.
Conclusions: Patient-derived MuSK antibodies can act either as MuSK agonist or MuSK antagonist, depending on the number of MuSK binding sites. Functional monovalency, induced by Fab-arm exchange in patient serum, makes MuSK IgG4 antibodies pathogenic.
Figures

References
-
- Hoch W, McConville J, Helms S, Newsom-Davis J, Melms A, Vincent A. Auto-antibodies to the receptor tyrosine kinase MuSK in patients with myasthenia gravis without acetylcholine receptor antibodies. Nat Med 2001;7:365–368. - PubMed
-
- McConville J, Farrugia ME, Beeson D, et al. . Detection and characterization of MuSK antibodies in seronegative myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol 2004;55:580–584. - PubMed
-
- Lighaam LC, Rispens T. The immunobiology of immunoglobulin G4. Semin Liver Dis 2016;36:200–215. - PubMed
-
- van der Neut Kolfschoten M, Schuurman J, Losen M, et al. . Anti-inflammatory activity of human IgG4 antibodies by dynamic Fab arm exchange. Science 2007;317:1554–1557. - PubMed
-
- Shiraishi H, Motomura M, Yoshimura T, et al. . Acetylcholine receptors loss and postsynaptic damage in MuSK antibody-positive myasthenia gravis. Ann Neurol 2005;57:289–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
