Trapped! A Critical Evaluation of Methods for Measuring Total Cellular Uptake versus Cytosolic Localization
- PMID: 30882208
- PMCID: PMC6527423
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00112
Trapped! A Critical Evaluation of Methods for Measuring Total Cellular Uptake versus Cytosolic Localization
Abstract
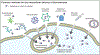
Biomolecules have many properties that make them promising for intracellular therapeutic applications, but delivery remains a key challenge because large biomolecules cannot easily enter the cytosol. Furthermore, quantification of total intracellular versus cytosolic concentrations remains demanding, and the determination of delivery efficiency is thus not straightforward. In this review, we discuss strategies for delivering biomolecules into the cytosol and briefly summarize the mechanisms of uptake for these systems. We then describe commonly used methods to measure total cellular uptake and, more selectively, cytosolic localization, and discuss the major advantages and drawbacks of each method. We critically evaluate methods of measuring "cell penetration" that do not adequately distinguish total cellular uptake and cytosolic localization, which often lead to inaccurate interpretations of a molecule's cytosolic localization. Finally, we summarize the properties and components of each method, including the main caveats of each, to allow for informed decisions about method selection for specific applications. When applied correctly and interpreted carefully, methods for quantifying cytosolic localization offer valuable insight into the bioactivity of biomolecules and potentially the prospects for their eventual development into therapeutics.
Figures
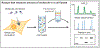


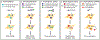
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

