SNP mutation-related genes in breast cancer for monitoring and prognosis of patients: A study based on the TCGA database
- PMID: 30883028
- PMCID: PMC6537087
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2065
SNP mutation-related genes in breast cancer for monitoring and prognosis of patients: A study based on the TCGA database
Abstract
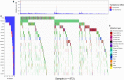
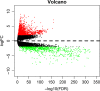
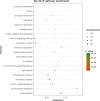
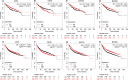
Advances in cancer biology have allowed early diagnosis and more comprehensive treatment of breast cancer (BC). However, it remains the most common cause of cancer death in women worldwide because of its strong invasiveness and metastasis. In-depth study of the molecular pathogenesis of BC and of relevant prognostic markers would improve the quality of life and prognosis of patients. In this study, bioinformatics analysis of SNP-related data from BC patients provided in the TCGA database revealed that six mutant genes (NCOR1, GATA3, CDH1, ATM, AKT1, and PTEN) were significantly associated with the corresponding expression levels of the proteins. The proteins were involved in multiple pathways related to the development of cancer, including the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, pertinent microRNAs, and the MAPK signaling pathway. In addition, overall survival and recurrence-free survival analysis revealed the close associations of the expression of GATA3, NCOR1, CDH1, and ATM with survival of BC patients. Therefore, detecting these gene mutations and exploring their corresponding expression could be valuable in predicting the prognosis of patients. The results of the high-throughput data mining provide important fundamental bioinformatics information and a relevant theoretical basis for further exploring the molecular pathogenesis of BC and assessing the prognosis of patients.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; biomarkers; breast cancer; prognosis; single nucleotide polymorphisms.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359‐386. - PubMed
-
- Smith TR, Miller MS, Lohman KK, Case LD, Hu JJ. DNA damage and breast cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24(5):883‐889. - PubMed
-
- Malins DC, Haimanot R. Major alterations in the nucleotide structure of DNA in cancer of the female breast. Cancer Res. 1991;51(19):5430‐5432. - PubMed
-
- Ding DP, He XF, Zhang Y. Lack of association between XPG Asp1104His and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a meta‐analysis of case‐control studies. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;129(1):203‐209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

