Increasing incidence of invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella infections in Queensland, Australia, 2007-2016
- PMID: 30883544
- PMCID: PMC6422252
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007187
Increasing incidence of invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella infections in Queensland, Australia, 2007-2016
Abstract
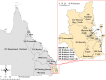
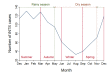
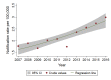
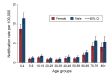
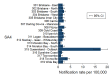
Nontyphoidal Salmonella is a major contributor to the global burden of foodborne disease, with invasive infections contributing substantially to illnesses and deaths. We analyzed notifiable disease surveillance data for invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella disease (iNTS) in Queensland, Australia. We used Poisson regression to estimate incidence rate ratios by gender, age group, and geographical area over 2007-2016. There were 995 iNTS cases, with 945 (92%) confirmed by blood culture. Salmonella Virchow accounted for 254 (25%) of 1,001 unique iNTS isolates. Invasive NTS disease notification rates peaked among infants, during the summer months, and in outback Queensland where the notification rate (95% CI) was 17.3 (14.5-20.1) cases per 100,000 population. Overall, there was a 6,5% annual increase (p<0.001) in iNTS disease incidence. In conclusion, high iNTS rates among males, infants, and the elderly require investigation of household level risk factors for NTS infection. Controlling Salmonella Virchow infections is a public health priority.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Vugia DJ, Samuel M, Farley MM, et al. Invasive Salmonella infections in the United States, FoodNet, 1996–1999: incidence, serotype distribution, and outcome. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 38 Suppl 3: S149–56. - PubMed
-
- Phu Huong Lan N, Le Thi Phuong T, Nguyen Huu H, et al. Invasive Non-typhoidal Salmonella infections in Asia: Clinical observations, disease outcome and dominant serovars from an infectious disease hospital in Vietnam. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016; 10(8): e0004857 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004857 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

