Maternal anemia and birth weight: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 30884493
- PMCID: PMC6422668
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212817
Maternal anemia and birth weight: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association between maternal anemia and low/insufficient birth weight.
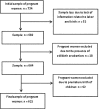
Design: A prospective cohort study of pregnant women who underwent prenatal care at the healthcare units in a municipality of northeast Brazil together with their newborn infants was carried out. The pregnant women were classified as having anemia when the hemoglobin level was below 11 g/dl. Infants who were born full term weighing less than 2500 grams were classified as low birth weight, and those weighing between 2500 and 2999 grams were classified as insufficient weight. The occurrence of maternal anemia and its association with birth weight was verified using crude and adjusted Relative Risk (RR) estimates with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs).
Results: The final sample was comprised of 622 women. Maternal anemia was considered a risk factor for low/insufficient birth weight, after adjusting the effect measurement for maternal age, family income, urinary infection, parity, alcoholic beverage consumption during pregnancy and gestational body mass index: RRadjusted = 1.38 [95% CI: 1.07 to 1.77].
Conclusions: Maternal anemia was associated with low/insufficient birth weight, representing a risk factor for the gestational outcomes studied.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determinants of low birth weight: a community based prospective cohort study.Indian Pediatr. 1994 Oct;31(10):1221-5. Indian Pediatr. 1994. PMID: 7875782
-
[Impact and changes of maternal hemoglobin on birth weight in pregnant women of Zhuang Nationality, in Guangxi].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Feb 10;38(2):154-157. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.02.004. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28231657 Chinese.
-
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN MATERNAL BODY MASS INDEX AND WEIGHT GAIN WITH LOW BIRTH WEIGHT IN EASTERN THAILAND.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2015 Nov;46(6):1085-91. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26867367
-
[Review by expert group in the diagnosis and treatment of anemia in pregnant women. Federación Mexicana de Colegios de Obstetricia y Ginecología].Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2012 Sep;80(9):563-80. Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2012. PMID: 23243836 Spanish.
-
Maternal Anemia during pregnancy and infant low birth weight: A systematic review and Meta-analysis.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2017 Mar;15(3):125-134. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28580444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of anemia severity levels among children aged 6-59 months in Ethiopia: Multilevel Bayesian statistical approach.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 13;13(1):4147. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20381-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36914676 Free PMC article.
-
Anemia during pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies.Front Glob Womens Health. 2025 Jan 31;6:1502585. doi: 10.3389/fgwh.2025.1502585. eCollection 2025. Front Glob Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 39959784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of anemia and associated risk factors among pregnant women in an urban community at the North of Saudi Arabia.J Prev Med Hyg. 2021 Sep 15;62(3):E653-E663. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.3.1880. eCollection 2021 Sep. J Prev Med Hyg. 2021. PMID: 34909493 Free PMC article.
-
Co-existence of maternal overweight/obesity, child undernutrition, and anaemia among mother-child pairs in Ethiopia.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024 Mar 7;4(3):e0002831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002831. eCollection 2024. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38452001 Free PMC article.
-
Disordered Eating Behaviors Are Associated with Gestational Weight Gain in Adolescents.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 13;13(9):3186. doi: 10.3390/nu13093186. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Meeting of Advisory Group on Maternal Nutrition and Low Birthweight Genebra: WHO; 2002 Internet: http://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/lbw_strategy_background.pdf (accessed 23 august 2017).
-
- Moraes IB. Risk factors for underweight at birth. Campinas, São Paulo: Universidade Estadual de Campinas, 2001.
-
- UNICEF. Low Birthweight: Country,regional and global estimates. New York: UNICEF; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical