Maternal anemia and birth weight: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 30884493
- PMCID: PMC6422668
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212817
Maternal anemia and birth weight: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association between maternal anemia and low/insufficient birth weight.
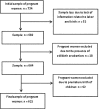
Design: A prospective cohort study of pregnant women who underwent prenatal care at the healthcare units in a municipality of northeast Brazil together with their newborn infants was carried out. The pregnant women were classified as having anemia when the hemoglobin level was below 11 g/dl. Infants who were born full term weighing less than 2500 grams were classified as low birth weight, and those weighing between 2500 and 2999 grams were classified as insufficient weight. The occurrence of maternal anemia and its association with birth weight was verified using crude and adjusted Relative Risk (RR) estimates with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs).
Results: The final sample was comprised of 622 women. Maternal anemia was considered a risk factor for low/insufficient birth weight, after adjusting the effect measurement for maternal age, family income, urinary infection, parity, alcoholic beverage consumption during pregnancy and gestational body mass index: RRadjusted = 1.38 [95% CI: 1.07 to 1.77].
Conclusions: Maternal anemia was associated with low/insufficient birth weight, representing a risk factor for the gestational outcomes studied.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Meeting of Advisory Group on Maternal Nutrition and Low Birthweight Genebra: WHO; 2002 Internet: http://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/lbw_strategy_background.pdf (accessed 23 august 2017).
-
- Moraes IB. Risk factors for underweight at birth. Campinas, São Paulo: Universidade Estadual de Campinas, 2001.
-
- UNICEF. Low Birthweight: Country,regional and global estimates. New York: UNICEF; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical