In House Validated UHPLC Protocol for the Determination of the Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Content in Virgin Olive Oil Fit for the Purpose of the Health Claim Introduced by the EC Regulation 432/2012 for "Olive Oil Polyphenols"
- PMID: 30884804
- PMCID: PMC6471533
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24061044
In House Validated UHPLC Protocol for the Determination of the Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Content in Virgin Olive Oil Fit for the Purpose of the Health Claim Introduced by the EC Regulation 432/2012 for "Olive Oil Polyphenols"
Abstract
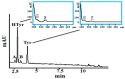
An ongoing challenge in olive oil analytics is the development of a reliable procedure that can draw the consensus of all interested parties regarding the quantification of concentrations above the required minimum value of 5 mg of bioactive "olive oil polyphenols" per 20 g of the oil, to fulfill the health claim introduced by the European Commission (EC) Regulation 432/2012. An in-house validated ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) protocol fit for this purpose is proposed. It relies on quantification of the total hydroxytyrsol (Htyr) and tyrosol (Tyr) content in the virgin olive oil (VOO) polar fraction (PF) before and after acidic hydrolysis of their bound forms. PF extraction and hydrolysis conditions were as previously reported. The chromatographic run lasts ~1/3 of the time needed under high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) conditions, this was also examined. Eluent consumption for the same piece of information was 6-fold less. Apart from being cost effective, a larger number of samples can be analyzed daily with less environmental impact. Two external curves, detection at 280 nm and correction factors for molecular weight difference are proposed. The method, which is fit for purpose, is selective, robust with satisfactory precision (percentage relative standard deviation (%RSD) values < 11%) and recoveries higher than 87.6% for the target analytes (Htyr, Tyr). Standard operational procedures are easy to apply in the olive oil sector.
Keywords: European Commission Regulation 432/2012; UHPLC; diode array detection; health claim; hydroxytyrosol; olive oil phenols; tyrosol; validation; virgin olive oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
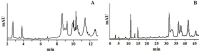
Similar articles
-
The EFSA Health Claim on Olive Oil Polyphenols: Acid Hydrolysis Validation and Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Determination in Italian Virgin Olive Oils.Molecules. 2019 Jun 10;24(11):2179. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112179. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31185655 Free PMC article.
-
Toward a Harmonized and Standardized Protocol for the Determination of Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Content in Virgin Olive Oil (VOO). The Pros of a Fit for the Purpose Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) Procedure.Molecules. 2019 Jul 2;24(13):2429. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132429. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31269664 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing analytical requirements to support health claims on "olive oil polyphenols" (EC Regulation 432/2012).J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Mar 26;62(12):2459-61. doi: 10.1021/jf5005918. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24576103
-
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols: Modulation of Cellular Pathways Related to Oxidant Species and Inflammation in Aging.Cells. 2020 Feb 19;9(2):478. doi: 10.3390/cells9020478. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32093046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olive Oil Polyphenols in Neurodegenerative Pathologies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1195:77-91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32633-3_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32468462 Review.
Cited by
-
The EFSA Health Claim on Olive Oil Polyphenols: Acid Hydrolysis Validation and Total Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Determination in Italian Virgin Olive Oils.Molecules. 2019 Jun 10;24(11):2179. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112179. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31185655 Free PMC article.
-
Valorization of monovarietal Nostrana di Brisighella extra virgin olive oils: focus on bioactive compounds.Front Nutr. 2024 Apr 4;11:1353832. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1353832. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38638290 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of the Sono-Heat-Exchanger in the Extra Virgin Olive Oil Extraction Process: End-User Validation and Analytical Evaluation.Molecules. 2019 Jun 27;24(13):2379. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132379. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31252634 Free PMC article.
-
On the Effect of Microwave Heating on Quality Characteristics and Functional Properties of Persimmon Juice and Its Residue.Foods. 2021 Nov 1;10(11):2650. doi: 10.3390/foods10112650. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34828930 Free PMC article.
-
Signal-On Fluorescent Imprinted Nanoparticles for Sensing of Phenols in Aqueous Olive Leaves Extracts.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 May 26;10(6):1011. doi: 10.3390/nano10061011. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32466364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Commission Regulation EC No. 2568/1991 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis. [(accessed on 11 February 2019)];Off. J. Eur. Union. 1991 L248:1–128. and amendments M1–M28. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:01991R2568....
-
- International Olive oil Council Testing Methods. [(accessed on 11 February 2019)]; Available online: http://www.internationaloliveoil.org/estaticos/view/224-testing-methods.
-
- Alimentarius C. Codex Standard for Olive Oils and Olive Pomace Oils. FAO; Rome, Italy: 1989. Codex Stan. 1981:33-1981. Rev.
-
- United States Department of Agriculture Olive Oil and Olive-Pomace Oil Grades and Standards. [(accessed on 11 February 2019)]; Available online: https://www.ams.usda.gov/grades-standards/olive-oil-and-olive-pomace-oil....
-
- European Commission Regulation EC No. 1308/2013 establishing a common organization of the markets in agricultural products and repealing Council Regulations (EEC) No 922/72, (EEC) No 234/79, (EC) No 1037/2001 and (EC) No 1234/2007. [(accessed on 11 February 2019)];Off. J. Eur. Union. 2013 L347:671–854. ANNEX XVI. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32013R1308.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

