Hesperetin, a Citrus Flavonoid, Attenuates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation, Apoptosis and Memory Impairments by Modulating TLR4/NF-κB Signaling
- PMID: 30884890
- PMCID: PMC6471991
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11030648
Hesperetin, a Citrus Flavonoid, Attenuates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation, Apoptosis and Memory Impairments by Modulating TLR4/NF-κB Signaling
Abstract
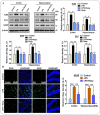
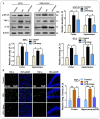
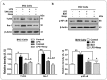
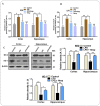
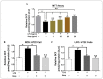
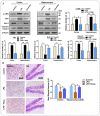
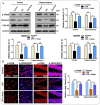
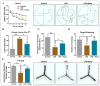
Glial activation and neuroinflammation play significant roles in apoptosis as well as in the development of cognitive and memory deficits. Neuroinflammation is also a critical feature in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer and Parkinson's diseases. Previously, hesperetin has been shown to be an effective antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. In the present study, in vivo and in vitro analyses were performed to evaluate the neuroprotective effects of hesperetin in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis and memory impairments. Based on our findings, LPS treatment resulted in microglial activation and astrocytosis and elevated the expression of inflammatory mediators such as phosphorylated-Nuclear factor-κB (p-NF-κB), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in the cortical and hippocampal regions and in BV2 cells. However, hesperetin cotreatment markedly reduced the expression of inflammatory cytokines by ameliorating Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4)-mediated ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1/glial fibrillary acidic protein (Iba-1/GFAP) expression. Similarly, hesperetin attenuated LPS-induced generation of reactive oxygen species/lipid per oxidation (ROS/LPO) and improved the antioxidant protein level such as nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Haem-oxygenase (HO-1) in the mouse brain. Additionally, hesperetin ameliorated cytotoxicity and ROS/LPO induced by LPS in HT-22 cells. Moreover, hesperetin rescued LPS-induced neuronal apoptosis by reducing the expression of phosphorylated-c-Jun N-terminal kinases (p-JNK), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)-associated X protein (Bax), and Caspase-3 protein and promoting the Bcl-2 protein level. Furthermore, hesperetin enhanced synaptic integrity, cognition, and memory processes by enhancing the phosphorylated-cAMP response element binding protein (p-CREB), postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95), and Syntaxin. Overall, our preclinical study suggests that hesperetin conferred neuroprotection by regulating the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway against the detrimental effects of LPS.
Keywords: LPS; hesperetin; memory Impairments; microglia/astrocytes; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; reactive oxygen species (ROS); tumor necrosis factor (TNF).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

