Structural plasticity of the hippocampus in response to estrogens in female rodents
- PMID: 30885239
- PMCID: PMC6423800
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-019-0442-7
Structural plasticity of the hippocampus in response to estrogens in female rodents
Abstract
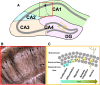
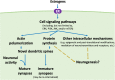
It is well established that estrogens affect neuroplasticity in a number of brain regions. In particular, estrogens modulate and mediate spine and synapse formation as well as neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. In this review, we discuss current research exploring the effects of estrogens on dendritic spine plasticity and neurogenesis with a focus on the modulating factors of sex, age, and pregnancy. Hormone levels, including those of estrogens, fluctuate widely across the lifespan from early life to puberty, through adulthood and into old age, as well as with pregnancy and parturition. Dendritic spine formation and modulation are altered both by rapid (likely non-genomic) and classical (genomic) actions of estrogens and have been suggested to play a role in the effects of estrogens on learning and memory. Neurogenesis in the hippocampus is influenced by age, the estrous cycle, pregnancy, and parity in female rodents. Furthermore, sex differences exist in hippocampal cellular and molecular responses to estrogens and are briefly discussed throughout. Understanding how structural plasticity in the hippocampus is affected by estrogens and how these effects can influence function and be influenced by other factors, such as experience and sex, is critical and can inform future treatments in conditions involving the hippocampus.
Keywords: Neurogenesis; aging; dendritic spines; depression; memory; parity; pregnancy; sex differences; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hippocampal learning, memory, and neurogenesis: Effects of sex and estrogens across the lifespan in adults.Horm Behav. 2015 Aug;74:37-52. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.05.024. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Horm Behav. 2015. PMID: 26122299 Review.
-
Habituation to novel stimuli alters hippocampal plasticity associated with morphine tolerance in male Wistar rats.Brain Res. 2025 Apr 15;1853:149508. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149508. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39954800
-
Influence of different estrogens on neuroplasticity and cognition in the hippocampus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct;1800(10):1056-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.01.006. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20100545 Review.
-
Rapid nongenomic modulation by neurosteroids of dendritic spines in the hippocampus: Androgen, oestrogen and corticosteroid.J Neuroendocrinol. 2018 Feb;30(2). doi: 10.1111/jne.12561. J Neuroendocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29194818 Review.
-
Endocrine regulation of cognition and neuroplasticity: our pursuit to unveil the complex interaction between hormones, the brain, and behaviour.Can J Exp Psychol. 2008 Dec;62(4):247-60. doi: 10.1037/a0014501. Can J Exp Psychol. 2008. PMID: 19071993 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased palmitoylation improves estrogen receptor alpha-dependent hippocampal synaptic deficits in a mouse model of synucleinopathy.Sci Adv. 2023 Nov 15;9(46):eadj1454. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj1454. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37976363 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the coding and non-coding RNA transcriptome expression profiles of hippocampus tissue in tx-J animal model of Wilson's disease.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 7;13(1):9252. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36503-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37286730 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol-mediated modulation of memory and of the underlying dendritic spine plasticity through the life span.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Apr;39(4):411-423. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-672. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 37966087 Review.
-
Concurrent Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Dorsal Hippocampal Activity Is Required for Estradiol-Mediated Effects on Object Memory and Spatial Memory Consolidation.eNeuro. 2019 Aug 20;6(4):ENEURO.0271-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0271-19.2019. Print 2019 Jul/Aug. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31431561 Free PMC article.
-
Isoflavone-Enriched Soybean Leaves (Glycine Max) Alleviate Cognitive Impairment Induced by Ovariectomy and Modulate PI3K/Akt Signaling in the Hippocampus of C57BL6 Mice.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 10;14(22):4753. doi: 10.3390/nu14224753. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432439 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

