Human iPSC-derived MSCs (iMSCs) from aged individuals acquire a rejuvenation signature
- PMID: 30885246
- PMCID: PMC6423778
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1209-x
Human iPSC-derived MSCs (iMSCs) from aged individuals acquire a rejuvenation signature
Abstract
Background: Primary mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are fraught with aging-related shortfalls. Human-induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived MSCs (iMSCs) have been shown to be a useful clinically relevant source of MSCs that circumvent these aging-associated drawbacks. To date, the extent of the retention of aging-hallmarks in iMSCs differentiated from iPSCs derived from elderly donors remains unclear.
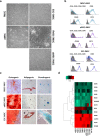
Methods: Fetal femur-derived MSCs (fMSCs) and adult bone marrow MSCs (aMSCs) were isolated, corresponding iPSCs were generated, and iMSCs were differentiated from fMSC-iPSCs, from aMSC-iPSCs, and from human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) H1. In addition, typical MSC characterization such as cell surface marker expression, differentiation capacity, secretome profile, and trancriptome analysis were conducted for the three distinct iMSC preparations-fMSC-iMSCs, aMSC-iMSCs, and ESC-iMSCs. To verify these results, previously published data sets were used, and also, additional aMSCs and iMSCs were analyzed.
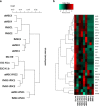
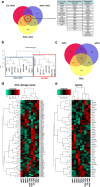
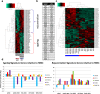
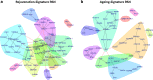
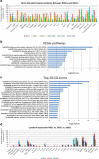
Results: fMSCs and aMSCs both express the typical MSC cell surface markers and can be differentiated into osteogenic, adipogenic, and chondrogenic lineages in vitro. However, the transcriptome analysis revealed overlapping and distinct gene expression patterns and showed that fMSCs express more genes in common with ESCs than with aMSCs. fMSC-iMSCs, aMSC-iMSCs, and ESC-iMSCs met the criteria set out for MSCs. Dendrogram analyses confirmed that the transcriptomes of all iMSCs clustered together with the parental MSCs and separated from the MSC-iPSCs and ESCs. iMSCs irrespective of donor age and cell type acquired a rejuvenation-associated gene signature, specifically, the expression of INHBE, DNMT3B, POU5F1P1, CDKN1C, and GCNT2 which are also expressed in pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs and ESC) but not in the parental aMSCs. iMSCs expressed more genes in common with fMSCs than with aMSCs. Independent real-time PCR comparing aMSCs, fMSCs, and iMSCs confirmed the differential expression of the rejuvenation (COX7A, EZA2, and TMEM119) and aging (CXADR and IGSF3) signatures. Importantly, in terms of regenerative medicine, iMSCs acquired a secretome (e.g., angiogenin, DKK-1, IL-8, PDGF-AA, osteopontin, SERPINE1, and VEGF) similar to that of fMSCs and aMSCs, thus highlighting their ability to act via paracrine signaling.
Conclusions: iMSCs irrespective of donor age and cell source acquire a rejuvenation gene signature. The iMSC concept could allow circumventing the drawbacks associated with the use of adult MSCs und thus provide a promising tool for use in various clinical settings in the future.
Keywords: Aged MSC; Aging; Fetal MSCs; Rejuvenation; Secretome; Transcriptome; iMSCs; iPSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Fetal femur-derived MSCs were obtained following informed, written patient consent. Approval was obtained by the Southampton and South West Hampshire Local Research Ethics Committee (LREC 296100). Adult mesenchymal stem cells, used for generation of iPSCs and iMSCs, were isolated from the bone marrow after written informed consent. The corresponding protocol was approved by the research ethics board of the Charite-Universitätsmedizin, Berlin (IRB approval EA2/126/07). Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from aged individuals was approved under the Southampton and South West Hampshire Local Research Ethics Committee (LREC 194/99). The Ethics commission of the medical faculty at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf also approved this study (Study number: 5013).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are Functionally and Genetically Different From Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Stem Cells. 2019 Jun;37(6):754-765. doi: 10.1002/stem.2993. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 30779868 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and proteomic profiles of fetal versus adult mesenchymal stromal cells and mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Mar 13;15(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03683-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38475970 Free PMC article.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus harrisii) Express Immunomodulatory Factors and a Tropism Toward Devil Facial Tumor Cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2020 Jan 1;29(1):25-37. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0203. Stem Cells Dev. 2020. PMID: 31709909
-
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Acquire Rejuvenation and Reduced Heterogeneity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 16;9:717772. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.717772. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34604216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
hiPSC-derived iMSCs: NextGen MSCs as an advanced therapeutically active cell resource for regenerative medicine.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Aug;20(8):1571-88. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12839. Epub 2016 Apr 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27097531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Senescent mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and restoring their cellular functions.World J Stem Cells. 2020 Sep 26;12(9):966-985. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v12.i9.966. World J Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 33033558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-Specific Integration of TRAIL in iPSC-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Targeted Cancer Therapy.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022 Mar 31;11(3):297-309. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szab031. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35267023 Free PMC article.
-
Retention of Somatic Memory Associated with Cell Identity, Age and Metabolism in Induced Pluripotent Stem (iPS) Cells Reprogramming.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020 Apr;16(2):251-261. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-09956-x. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020. PMID: 32016780 Review.
-
Application of Patient-Specific iPSCs for Modelling and Treatment of X-Linked Cardiomyopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 29;22(15):8132. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158132. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 27;22(5):2410. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052410. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33673711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

