XPG-related nucleases are hierarchically recruited for double-stranded rDNA break resection
- PMID: 30885940
- PMCID: PMC6514642
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005415
XPG-related nucleases are hierarchically recruited for double-stranded rDNA break resection
Abstract
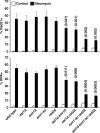
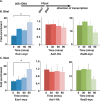
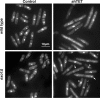
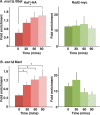
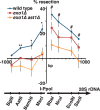
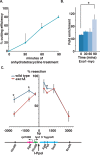
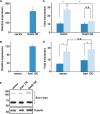
dsDNA breaks (DSBs) are resected in a 5'→3' direction, generating single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). This promotes DNA repair by homologous recombination and also assembly of signaling complexes that activate the DNA damage checkpoint effector kinase Chk1. In fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe), genetic screens have previously uncovered a family of three xeroderma pigmentosum G (XPG)-related nucleases (XRNs), known as Ast1, Exo1, and Rad2. Collectively, these XRNs are recruited to a euchromatic DSB and are required for ssDNA production and end resection across the genome. Here, we studied why there are three related but distinct XRN enzymes that are all conserved across a range of species, including humans, whereas all other DSB response proteins are present as single species. Using S. pombe as a model, ChIP and DSB resection analysis assays, and highly efficient I-PpoI-induced DSBs in the 28S rDNA gene, we observed a hierarchy of recruitment for each XRN, with a progressive compensatory recruitment of the other XRNs as the responding enzymes are deleted. Importantly, we found that this hierarchy reflects the requirement for different XRNs to effect efficient DSB resection in the rDNA, demonstrating that the presence of three XRN enzymes is not a simple division of labor. Furthermore, we uncovered a specificity of XRN function with regard to the direction of transcription. We conclude that the DSB-resection machinery is complex, is nonuniform across the genome, and has built-in fail-safe mechanisms, features that are in keeping with the highly pathological nature of DSB lesions.
Keywords: Checkpoint; DNA Damage Response; DNA Repair; DNA damage response; DNA recombination; DNA repair; Schizosaccharomyces pombe; XPG-Related Nuclease; cell cycle; chromosomes.
© 2019 Barnum et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

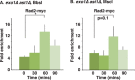
Similar articles
-
Initiation of DNA damage responses through XPG-related nucleases.EMBO J. 2013 Jan 23;32(2):290-302. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.322. Epub 2012 Dec 4. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23211746 Free PMC article.
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe KAT5 contributes to resection and repair of a DNA double-strand break.Genetics. 2021 May 17;218(1):iyab042. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab042. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33723569 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc24 Is Essential for Long-range End Resection in the Repair of Double-stranded DNA Breaks.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 25;291(48):24961-24973. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.755991. Epub 2016 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27729451 Free PMC article.
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Assays to Study Mitotic Recombination Outcomes.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 10;11(1):79. doi: 10.3390/genes11010079. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The conserved histone variant H2A.Z illuminates meiotic recombination initiation.Curr Genet. 2018 Oct;64(5):1015-1019. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0825-9. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29549582 Review.
Cited by
-
BMAL1 collaborates with CLOCK to directly promote DNA double-strand break repair and tumor chemoresistance.Oncogene. 2023 Mar;42(13):967-979. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02603-y. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36725890 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the nucleolar responses to DNA double-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 25;48(17):9449-9461. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa713. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32857853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of XPG rs2094258 polymorphism with gastric cancer prognosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 14;25(34):5152-5161. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5152. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31558863 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and Analysis of dsDNA Breaks for Checkpoint and Repair Studies in Fission Yeast.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2267:191-205. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1217-0_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33786793
-
The Role of RNA in DNA Breaks, Repair and Chromosomal Rearrangements.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 9;11(4):550. doi: 10.3390/biom11040550. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33918762 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

